Search engine optimization (SEO) is all about understanding different Google ranking factors so you can work on them and improve your site’s ranking and search visibility.
The issue is that Google has kept its ranking factors and signals hidden (like any other search engine).
This makes it hard to decode how Google works.
Thankfully, there’s a lot of information and data out there that has revealed some of the key ranking signals that Google uses.
This article explores the top Google ranking factors backed by evidence from supporting studies to help you improve your site’s ranking by following simple rules.
What Is a Google Ranking Factor?
A ranking factor is a variable used by Google to rank web pages on its search result page for a search query. It’s part of a bigger algorithm that consists of numerous signals and factors that are determined and evaluated each time a search query has to be addressed by Google.
Here’s what Google officially says about it:
Google uses automated ranking systems that look at many factors and signals about hundreds of billions of web pages and other content in our Search index to present the most relevant, useful results, all in a fraction of a second.
These factors and signals are broadly known as ranking factors.
If you are planning to improve the ranking of your site for a specific keyword, knowing these ranking factors will help you optimize your website to improve search visibility.
Google has kept these factors secret. It doesn’t share the exact list publicly.
We know from data, experimentation, analysis, and other sources most of these signals.
Types of Google Ranking Factors

Google uses a range of factors to determine different parts of your website:
- On-page ranking factors: These signals check the on-page SEO of your site such as HTML tags and content. Google uses these factors to rank sites based on their on-page optimization. On-page ranking factors are in your control and you can manage them.
- Off-page ranking factors: These include ranking signals that are off your website such as backlinks. These ranking factors aren’t in your control as most of these depend on how others engage with your site.
- Technical ranking factors: These factors look at your site’s technicalities such as crawling and indexing. Most of these signals are well within your control.
- Local ranking factors: Google uses additional factors to evaluate local businesses and sites that operate in a specific geographic location such as a physical retail outlet. Local ranking factors consist of a mix of signals that are within your control and some of them happen off your website.
These four ranking factors are used collectively for all websites. Local ranking factors are used specifically for location-based businesses and services along with other 3 types.
Top Google Ranking Factors
Here’s a list of the top Google ranking factors that you should focus on in 2025 to boost your rankings and drive more organic traffic to your website:
1. Content Quality
Content happens to be the most critical ranking signal that Google uses for all types of websites globally. It has one of the highest weightage among ranking factors.
Why?
Because content is what defines the quality of experience users get from a website.
A study reported that high quality content creation has a 21% impact on your rankings in Google making it a top ranking factor in 2025 and beyond:
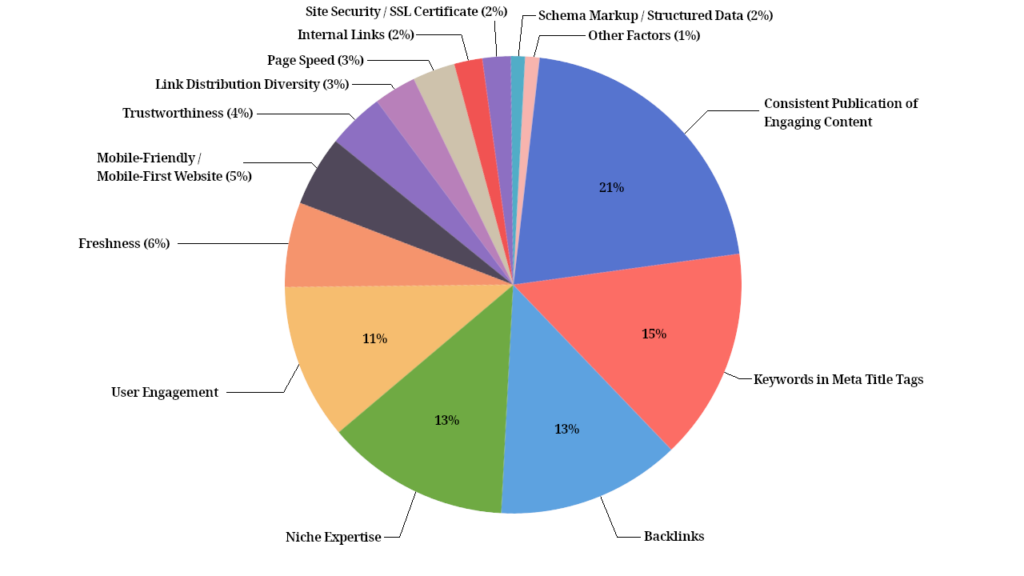
According to Semrush Google Ranking Report 2024, Google uses a wide range of content factors that are correlated to SERPs. Here’s a breakdown of top content factors that have a positive correlation with position on SERP:
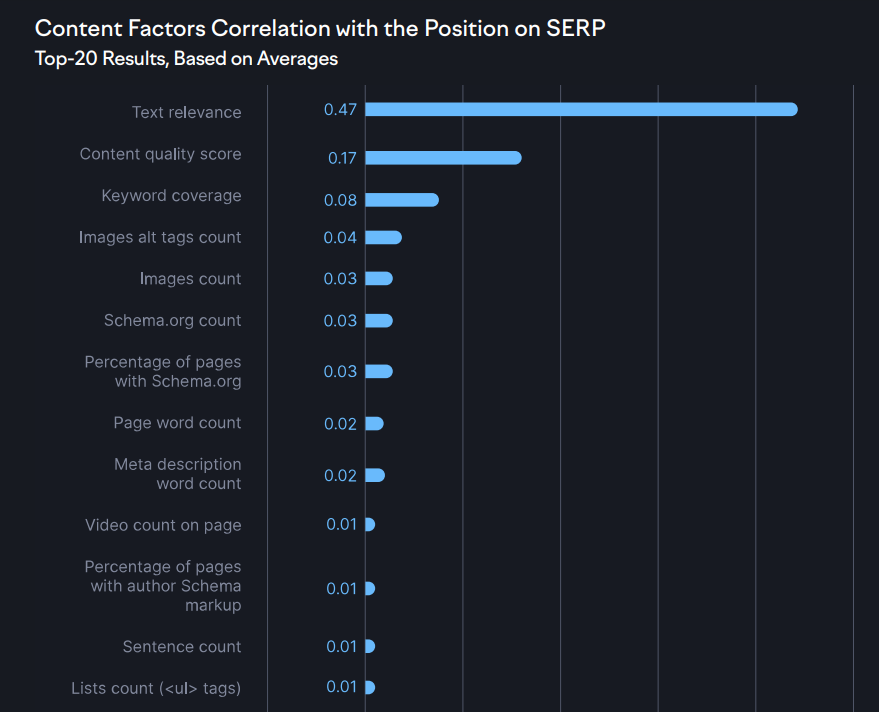
Text relevance has the highest correlation making it the top content factor with the highest impact. It refers to the relevance of your content with the search query. The content needs to cover all the details and the article needs to be extremely detailed.
You need to answer all the relevant search queries that a reader might have so that readers leave fully satisfied.
Content quality is the second top factor that has a direct impact on search rankings. Google has clearly stated guidelines on what type of content it considers quality content. It needs to be helpful, reliable, and people-first.
The content essentially needs to demonstrate experience, expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness (E-E-A-T).
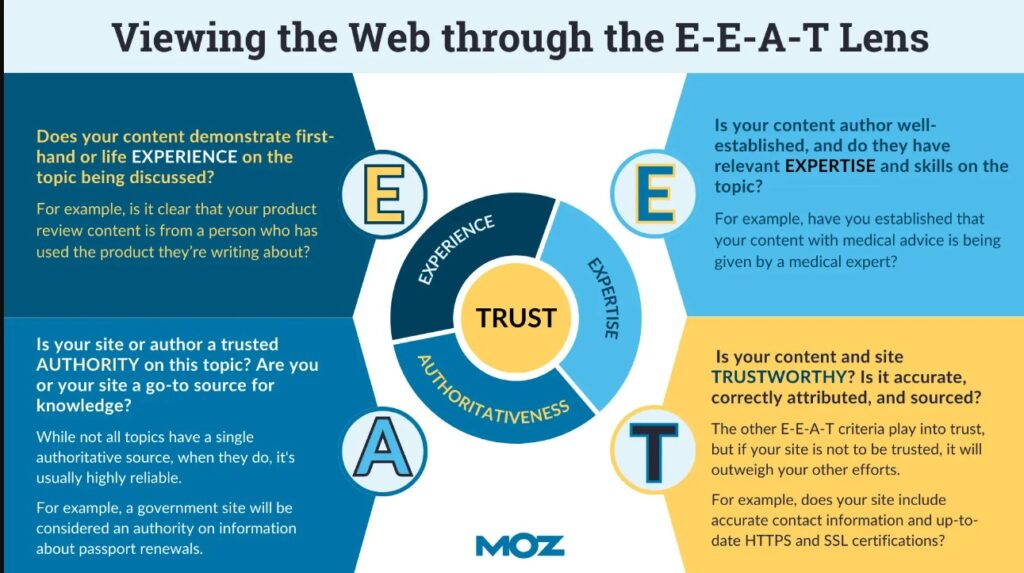
Quality content isn’t just limited to the content itself, rather it includes several other components such as page layout, UX, searcher satisfaction, design, and much more.
Keyword coverage is the third most important content ranking factor. It includes the number of keywords your content covers. The more keywords your content covers, the better. It is an indication that you have covered the topic comprehensively touching all the related concepts and ideas.
Other factors that Google uses to determine the quality of content on your site include:
- Number of image alt tags
- Number of images on the page
- Schema.org count
- Percentage of pages that have schema.org enabled
- Number of words
- Meta description word count
- Number of videos on the page
- Percentage of pages having author markup
- Total sentence count
- The number of lists on the page.
All of these subfactors are used collectively to determine the quality of content for a given webpage.
2. Number of Backlinks
The number of links your site has is a major off-page ranking factor that determines the popularity of your website. More backlinks mean high popularity as Google considers each backlink as a vote.
Backlinks, like content, are a broad factor that constitutes multiple metrics and signals that are all collectively related to position in SERPs.
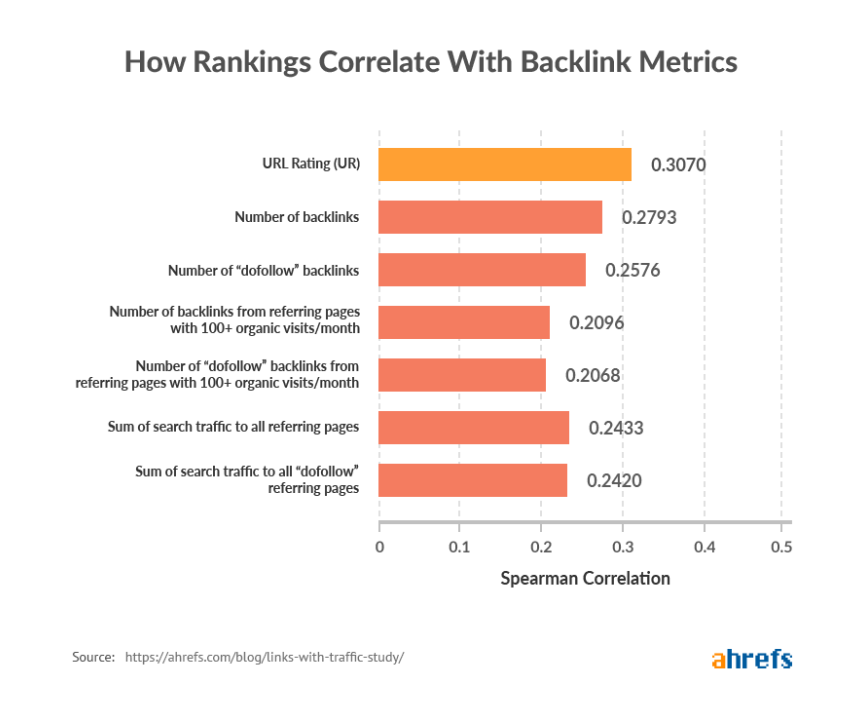
Ahrefs reported a list of backlink metrics that correlated with rankings that includes URL rating (an internal metric used by Ahrefs for measuring the rating of a specific URL), number of backlinks, number of dofollow backlinks, and others as shown below (with correlations):
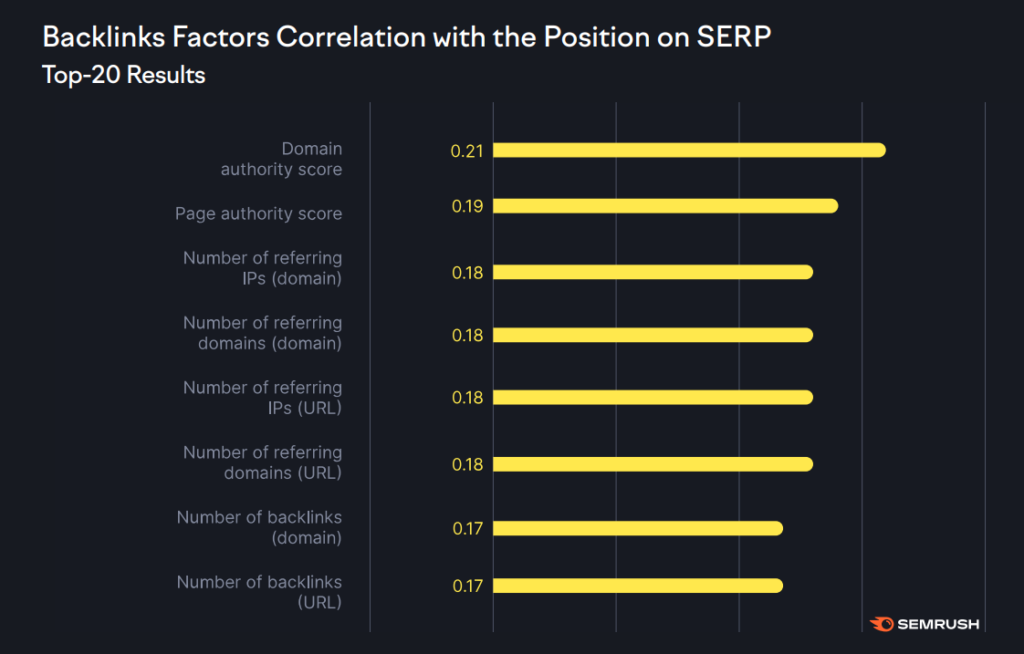
Semrush identified most of these signals in its report. Domain authority (which is a Semrush metric to measure the authority of a domain) has the highest correlation with rankings followed by page authority (Semrush metric for page authority), number of referring IPs, number of referring domains, and others:
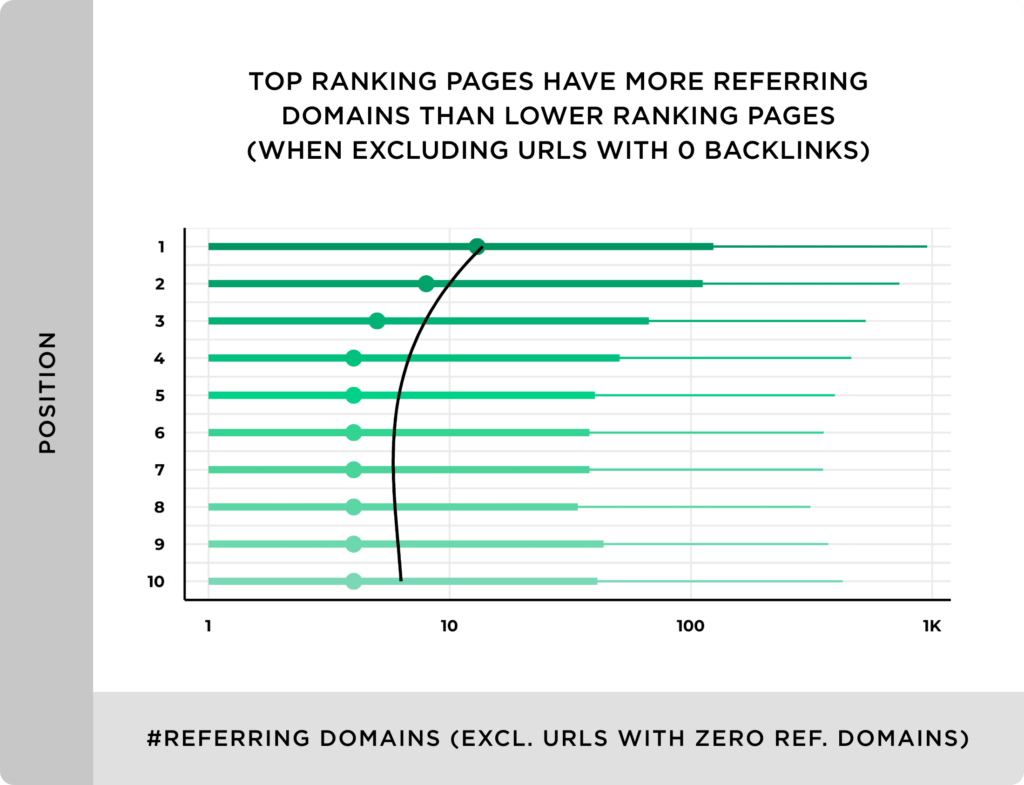
A study by Backlinko (part of Semrush) reported that pages having more referring domains have a higher ranking than sites with low number of referring domains:
These studies endorse two things:
- Backlinks have a major role in website ranking and Google uses them to determine SERPs
- It is a broad factor that consists of multiple subfactors that are all correlated with rankings.
One certain thing is that Google doesn’t treat all backlinks equally.
Backlinks are valued individually based on multiple sub-factors.
To help you better understand how Google uses backlinks as a ranking factor, here’s a list of all the signals and factors that Google potentially uses to evaluate the strength of backlinks your site has.
- Domain authority (this can be measured via any SEO tool)
- Page authority
- Number of referring domains (including unique referring domains)
- Number of backlinks
- Number of do-follow backlinks
- Referring IPs
- Number of backlinks from referring domains and pages with 100+ organic traffic per month
- The sum of traffic to all referring pages and domains.
All the popular SEO tools track and report all these backlink metrics. It isn’t all that hard to track these metrics and figure out where your website stands and how to improve its backlink profile.
3. User Experience
Your site’s UX is an important ranking factor that Google values a lot.
A few years back, Google was very particular about page load speed as it was directly related to the experience a visitor receives. Later, Google introduced Core Web Vitals which is a collection of 3 variables measuring UX collectively.
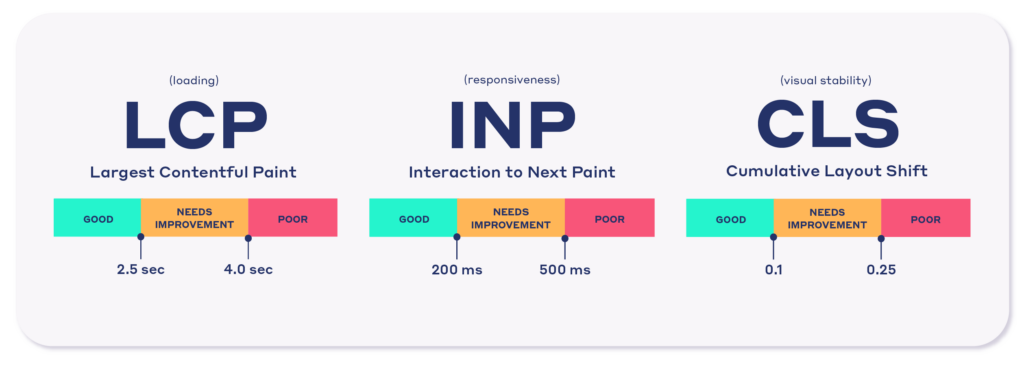
You can read more about Core Web Vitals here and here.
According to Google, site owners need to achieve a good score for Core Web Vitals and must measure it through the Search Console. Interestingly, Google says that Core Web Vitals is a measure of UX and scoring high on it doesn’t mean higher rankings.
Semrush study reported that Interaction to Next Paint (INP) is the only Core Web Vitals metric that is correlated with SERP position. While the other two have a negative correlation with rankings (LCP and CLS):
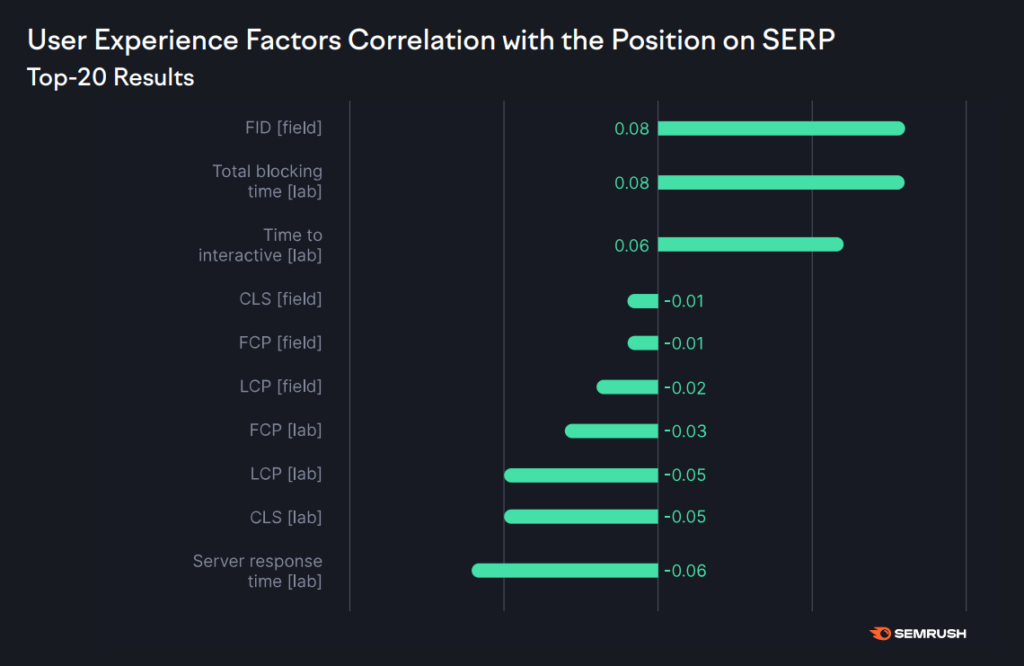
The First Contentful Paint (FID) is now replaced by Interaction to Next Paint (INP) which measures the time taken by the browser to respond to a user action. The more time a user has to wait after performing a task, the poorer the UX.
The correlation is quite low indicating that the impact of having a good INP score is minimal on rankings.
The other two metrics do not correlate with rankings.
This confirms that Google correctly stated that having a good Core Web Vitals score doesn’t guarantee a high ranking.
Google uses other UX ranking signals and factors that include:
- User interaction
- Organic CTR
- Pogo sticking
- Number of bookmarks
- Dwell time.
Generally, these UX ranking factors don’t have a high impact on rankings when compared with content and backlinks. A rule of thumb is that sites that have great content and lots of backlinks will naturally deliver a great UX.
Since content and backlinks carry more weight, they are always given preference over UX.
You can’t rank a site on the first page with poor content and no backlinks. You can rank a site with good content and backlinks but with poor UX.
Does this mean you should ignore UX?
Never.
Because it is associated with other Google ranking factors …
4. User Signals
Google uses behavioral data that mostly includes user interaction and engagement with a website as a ranking factor. These factors are collectively known as user signals.
Clicks, for instance, are known to have a slight impact on rankings. Google doesn’t use such users’ signals as primary ranking factors, but they do have an impact (much smaller though).
For instance, if a website receives 200 organic clicks for a certain search query and another site receives 100 clicks for the same query, Google will push the first site to the top position. This is because it assumes that it serves user query and intent better as a lot of people click it.
Then, Google will monitor the behavioral data of these 200 clicks. It will see how much time people spend on a site, how many click the back button and return to SERPs, what percentage of people re-run the same query again, and so on.
Remember, Google doesn’t have a full picture of how users interact with your site as it can’t track everything. However, it can track them when they are using Google Search and other Google products.
Direct traffic share and time on site are the two major user signals that have a positive correlation with rankings.
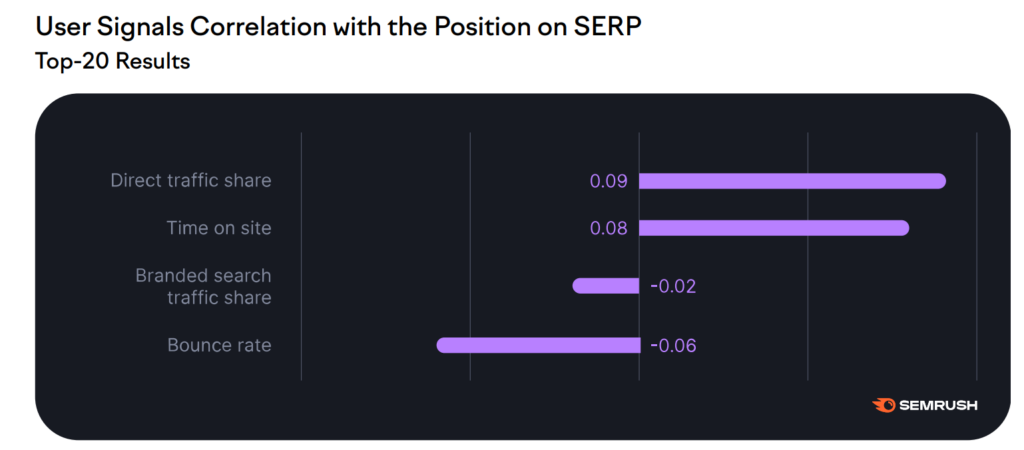
Direct traffic share of top sites is usually high. Such as Apple and Microsoft. Google ranks such websites high in SERPs that have a more direct traffic percentage. This indicates popularity and the algorithm favors and values it.
Time spent on site and bounce rate are also important user signals that impact rankings. Their impact is on the low side.
5. Organic Traffic
One of the best ways Google serves relevant and quality search results to searchers is by ranking sites based on organic traffic.
A site or a specific URL with high organic traffic is more likely to reach the top position in SERPs.
Why?
Because Google’s algorithm considers it to be of high quality that people tend to like. Organic CTR is used to determine the organic traffic of a search result.
For instance, if a certain search result on the first page gets more clicks than other results on the same page for a specific query, Google will push it to the first spot for the particular query.
This, however, doesn’t work backward.
A web page having high organic traffic might get demoted if it has a high bounce rate or if it performs poorly in terms of UX.
Just because a page has high organic traffic doesn’t mean it will stay at the top. The content needs to address the query completely and must provide an exceptional experience to the users.
Google uses a wide range of organic traffic factors to determine rankings in SERPs. The organic traffic of the URL is the main factor having a 0.33 correlation with the position in SERPs:
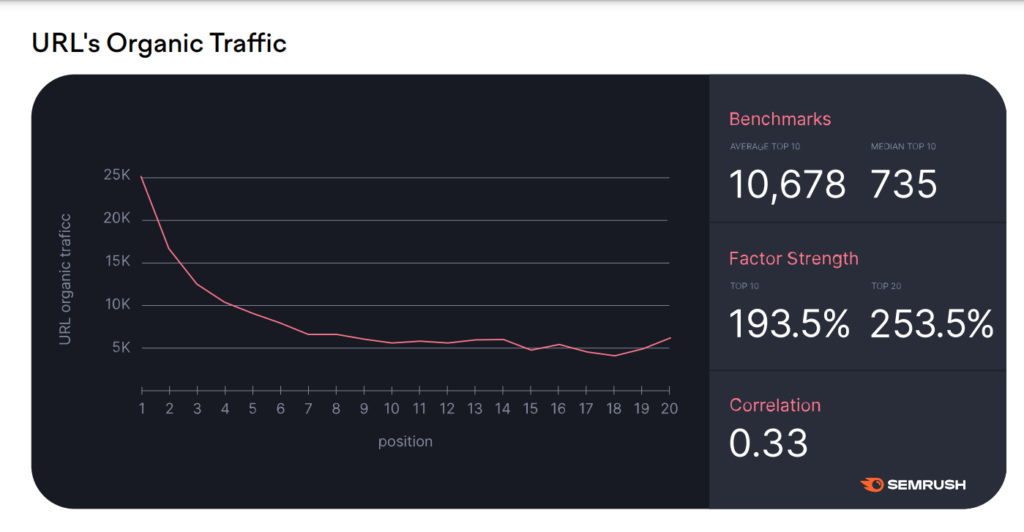
Other signals and factors include:
- Domain’s organic traffic
- Organic position of the URL
- Domain organic position in SERPs
- Domain appearance in images
- Domain and URL appearance in featured snippets
- Star ratings for domain and URL
- Domain age
- Repeat traffic to domain and URL.
Google uses a lot of ranking factors to evaluate the historical data about your domain and URL and their performance in SERPs. This is one reason sites with a history of high organic traffic tend to rank for any new content they publish without any marketing.
On the flip side, sites with low organic traffic find it extremely hard to make it to the first page of Google for any keyword.
6. Content Freshness
Content freshness is a different ranking factor than the quality of content you have on your site.
According to First Page Sage, content freshness has a 6% weightage as a ranking factor. It isn’t used as a ranking factor for all types of content, rather it is specifically used for certain content types known as Query Deserves Freshness (QDF).
QDF is a confirmed ranking factor focused on showing the most recent search results to people. For instance, for someone who is searching for an upcoming event in Vegas, Google will show the most recent and fresh content published or updated in the past few hours.
Content freshness applies to certain query types and industries more than others such as:
- Hot and trending topics
- News
- Recurring events
- Reviews and other content that needs to be updated.
Theoretically, you need to update and refresh all types of content. For instance, a blog post on losing belly fat with apples might not need fresh content as these methods don’t change.
But someone who’s looking at search results with one post from 2015, another from 2017, and one from 2024 – the user is more likely to click the most recent search result.
It triggers corresponding ranking factors like organic traffic, UX, behavioral data, etc. Google values fresh content more than old content (even if they both talk about the same thing).
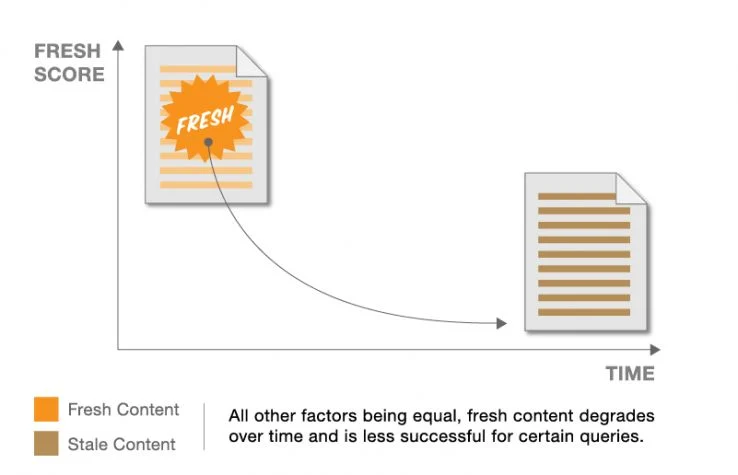
If you run a search query for pretty much anything in Google, more than 90% of search results will be from the past two years. This shows the importance of freshness as a ranking factor.
Google uses a wide range of sub-signals to monitor content freshness and rank sites accordingly:
- Date of content creation and publication
- The amount of changes made to the original content (fewer vs. major changes)
- Core content changes
- The frequency of changes made over a period of time
- Rate of new backlink acquisition.
You need to update and refresh content with a high frequency multiple times a year to improve and retain rankings.
7. Keyword in Title and URL
This might sound boring and outdated in a world where search engines use LSI and advanced machine learning to understand search queries and user intent. Having the exact keyword in the title and URL are both Google ranking signals.
The keyword in the title is the second highest weightage among all Google ranking factors (15%) which has a small positive correlation with rankings. The same goes for keywords in the URL:
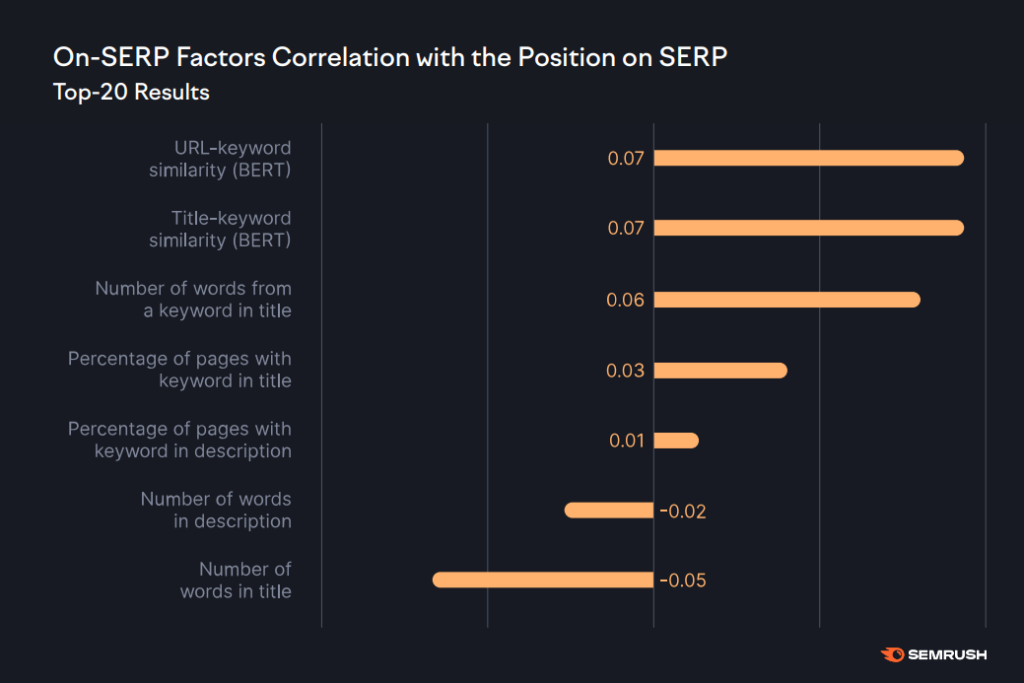
Top ranking pages, especially those in positions 1-3, in Google SERPs have keywords in their titles and URLs. Even if it’s the exact same keyword, it is somewhat related to the search query.
Here’s an example:
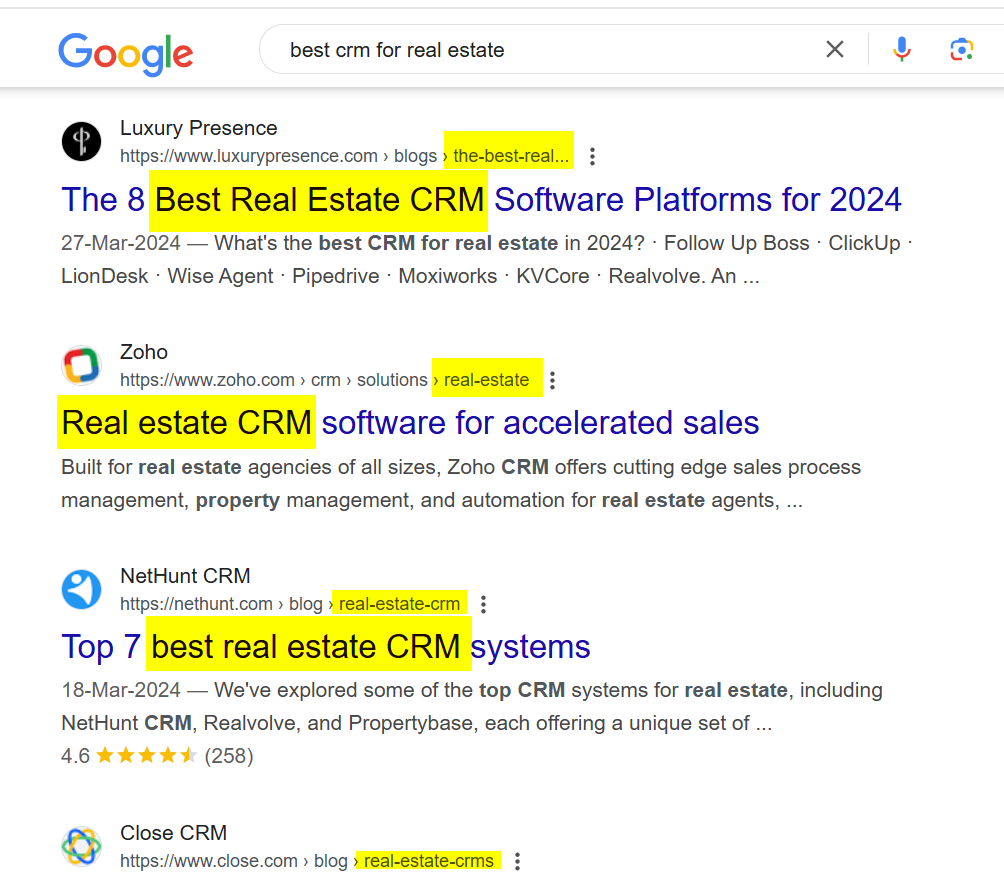
The keyword in the title makes your URL relevant to the search query and leads to high CTR – which leads to higher rankings as Google uses it as a ranking signal too.
Ambiguous, unclear, hyped, and non-descriptive titles might drive clicks, but they are bad at retaining visitors. It leads to a high bounce rate and poor UX leading to demotion in SERPs.
Try adding relevant, primary keyword in the title and URL to rank for the right search terms and drive relevant traffic.
Miscellaneous Google Ranking Factors
There are several other signals that Google uses to determine SERP rankings. These are either indirect ranking factors (that don’t have a direct impact on rankings) or have a small impact on rankings:
- Site architecture is an indirect ranking factor that performs two key functions. It helps Google bots crawl your site and it improves UX by helping site visitors navigate and find what they are looking for.
- Internal links are direct ranking factor that perform several functions – besides having a direct impact on rankings. They improve site navigation, structure, architecture, UX, and organization.
- Mobile responsiveness impacts ranking but its impact is too low. It’s embedded within the Core Web Vitals and isn’t monitored as a standalone ranking signal.
- Website accessibility is part of UX. Google doesn’t directly use it to rank websites in SERPs, but since it has a huge impact on user engagement, it gives essential signals to Google. For instance, if your site isn’t accessible to everyone, it might have a higher bounce rate than most of the other sites and Google will treat your site as low quality that fails to retain visitors. It will negatively impact rankings.
- Social signals are an indirect ranking factor that Google uses to determine your site’s popularity. If your site goes viral on social media, it will have a spike in direct and referral traffic. Google uses these signals to promote a site in SERPs considering it to be of high value and popular.
- Schema markup is a ranking factor for some types of sites such as ecommerce sites. It provides additional information to users in SERPs and to search crawlers. Anything that improves UX plays a role in ranking.
- Keyword in heading tags is a direct ranking factor. Google uses it to match content to search queries and serve relevant results.
- Content length is a ranking factor. The average word count of top ranking pages is 1,400 words which indicates that Google consistently looks at the word count for ranking sites.
Final Thoughts
Google uses at least 200 known ranking factors. In reality, it uses much more.
It’s a complex system of algorithms and machine learning that monitors Google’s database in real-time to furnish search queries. It’s believed that the weightage given to each factor isn’t constant. The weights keep changing depending on a different set of variables.
As a marketer and a business owner, your best bet is to stick with the most important ranking factors covered in this article.
The two core factors are content and backlinks.
If you can cover these two – the remaining ones will follow.
Create high quality content for humans, keep updating it regularly, and acquire backlinks naturally to promote your content.
Follow the remaining ranking factors and you can outrank your competitors in SERPs quite easily.
Featured Image: Pexels