Metrics help you measure performance. When you invest money in SEO, you must use the right metrics to track SEO effectiveness.
There are numerous SEO metrics out there that you can track, but you don’t have to necessarily monitor all of them. It’ll lead you nowhere if you track hundreds of SEO metrics. A better, smarter approach is to measure metrics that are most important for your business and represent SEO performance accurately.
And leave all the rest.
This article explores the 7 SEO metrics you should track and 3 metrics that you shouldn’t. Let’s explore the metrics and see how you can optimize your limited resources.
What is an SEO Metric?
An SEO metric is a key performance indicator (KPI) that measures and tracks the SEO performance of your website. Metrics show SEO performance quantitatively based on data from your analytics or SEO tool.
For example, the number of organic visitors per day is a classical SEO metric that tells you how many visitors per day your website receives from search engines.
SEO metrics help you in multiple ways:
- You can track the performance of your SEO efforts via metrics
- Metrics help you make data-based decisions
- You can find SEO opportunities and work on the weaknesses
- Compare your SEO standing with industry standards through benchmarks
- Prove SEO ROI easily.
You have to choose and track the most appropriate metrics to measure SEO performance accurately. Not all SEO metrics are worth measuring.
Below is a list of the SEO metrics you should and shouldn’t track so that you can optimize your resources and invest energy and time where it matters the most.
7 SEO Metrics to Track
Here’s a list of SEO KPIs you must measure:
1. Organic Traffic
It is the core SEO metric that shows the total traffic received from search engines. This is the first indicator that shows if your SEO strategy is working correctly.
You can track organic traffic through Google Analytics under Examine user behavior > Overview:
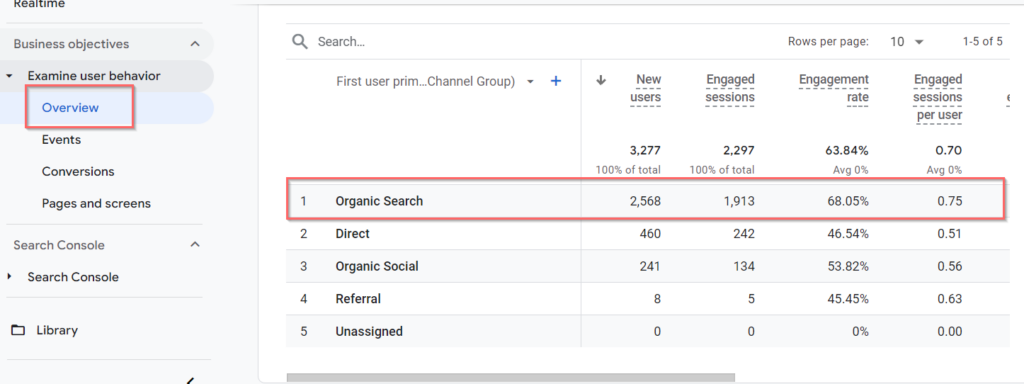
Select the primary source to check detailed overview of organic traffic received from different search engines:
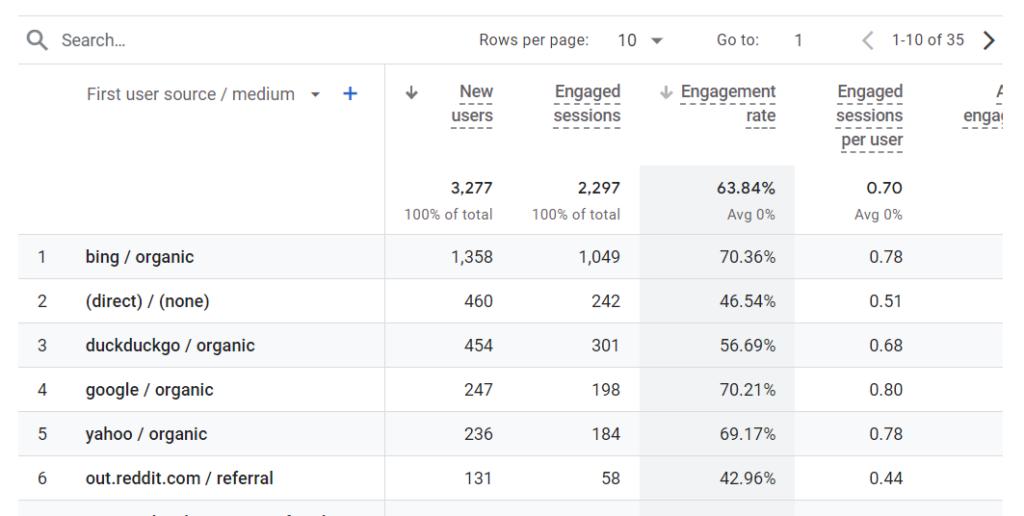
You can filter search results by selecting secondary metrics such as engagement rate or new users to dig deep and find out which search engine drives the most traffic.
Google Search Console is another free tool that you can use to find organic clicks you receive from Google specifically. Select Total clicks and set your desired date to view clicks from Google search:
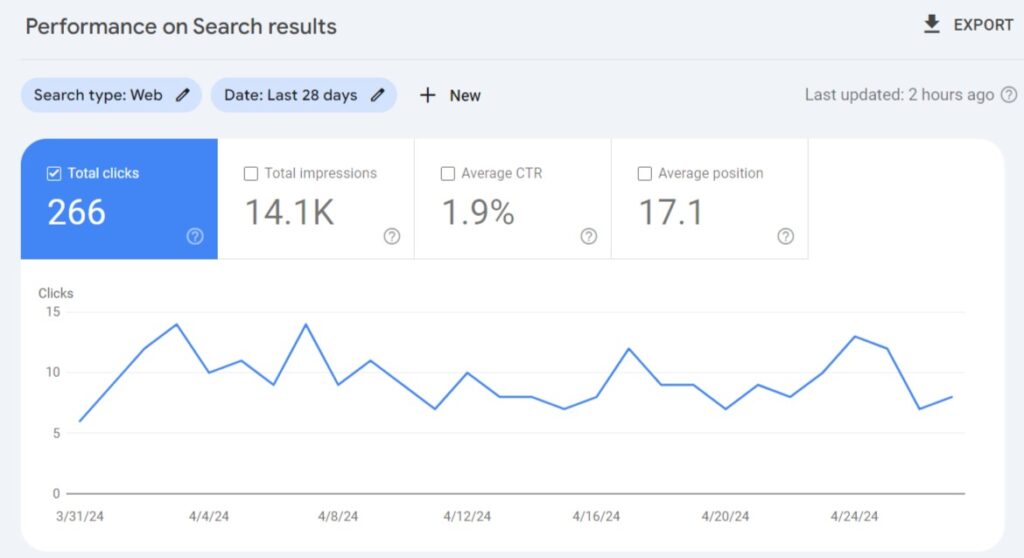
You can scroll down to see top queries, pages, countries, and devices to filter results:
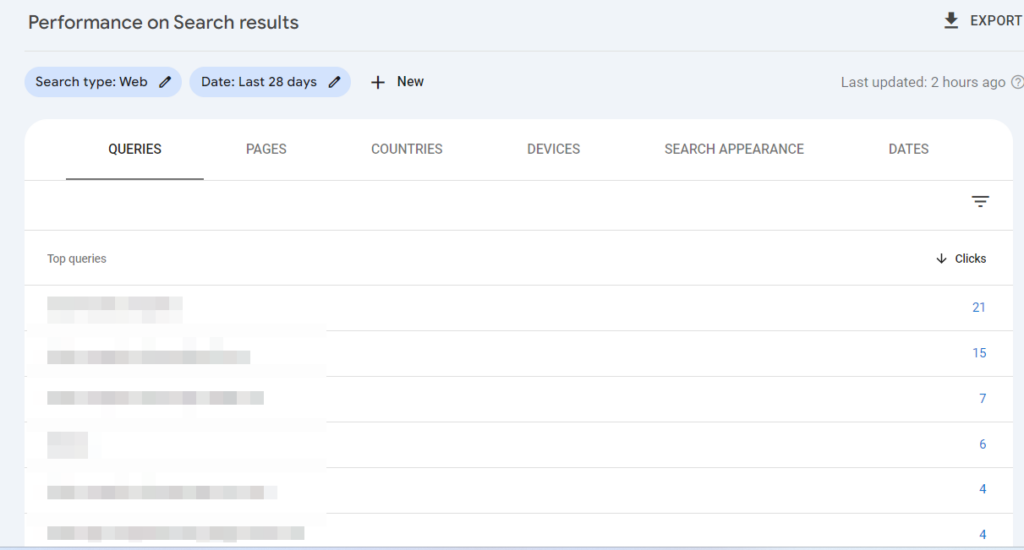
An increase in organic traffic indicates your SEO efforts are working well. A decline in organic traffic needs to be further investigated as it is a sign that something isn’t right.
2. Keyword Rankings
You have to track the performance of individual keywords that you target via your SEO campaigns. Keyword ranking tells you the current and historical ranking in SERPs for any given keyword that is important for your business.
It is an important SEO metric for two main reasons:
- Keyword ranking tells you how effective your SEO campaigns are and what actions lead to significant changes in keyword rankings
- It helps you figure out what works and what doesn’t to move the needle.
If you don’t track keyword ranking, you’ll see great SEO performance, but it’ll get challenging to figure out which SEO technique works best and which one doesn’t. Keyword positions in SERPs give you detailed insights and you can link ranking fluctuations with corresponding SEO techniques and tactics.
For example, if you revised and updated a blog post for freshness and it moved your keyword to the first place in SERPs, you can replicate the process for other posts for massive success.
There are two ways to track keyword rankings:
You can use Google Search Console to track the average position of all the keywords your website or a specific page rank for. You can filter results to see average impressions, clicks, and CTR too. Check actual search queries (not keywords) that your website (or pages) rank for.
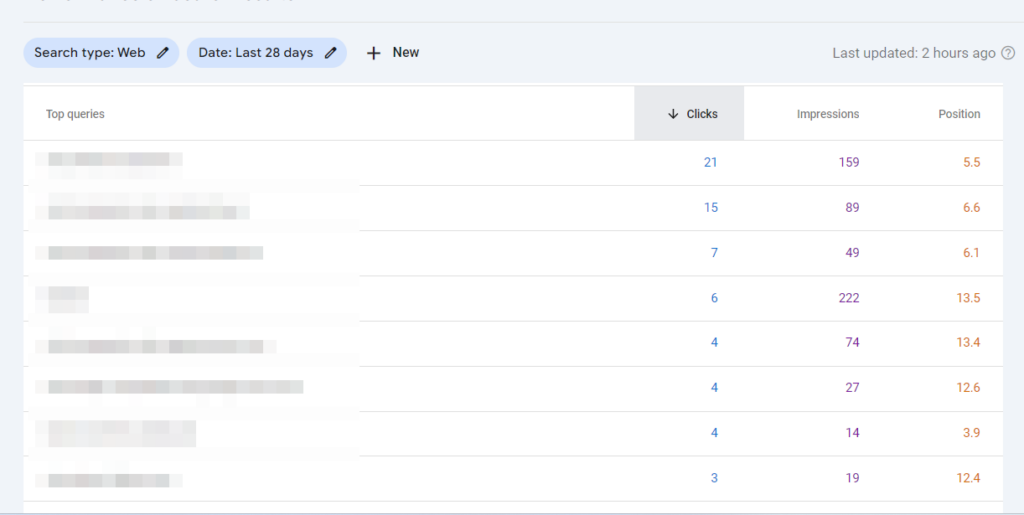
You can also inspect the historical ranking of the search queries at individual and page levels. It is a free method and works great.
You can use a paid keyword ranking tool like Ahrefs, Semrush, Moz, and others. These tools offer more detailed insights that you don’t get with Search Console. You can track individual keywords across locations, you can check ranking for images and featured snippets, and check the traffic you drive from these keywords.
Here’s a glimpse of Ahrefs rank tracker tool:
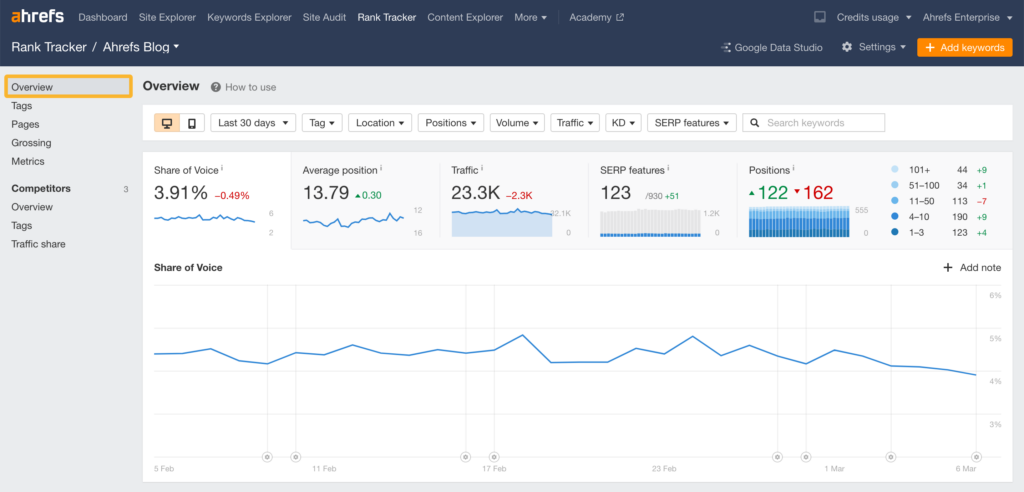
If you can afford a premium rank tracking tool, go for it. If you can’t, use Google Search Console for authentic and accurate position tracking.
3. Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals (CWV) is a set of 3 UX metrics that are used by Google to determine the usefulness and experience of a web page. These are ranking factors but don’t have a huge impact on rankings.
CWV isn’t a typical SEO metric as it tracks UX and not search appearance specifically, but since UX plays a massive role in search visibility and rankings, you should track this metric for SEO.
You can analyze CWV in your Google Search Console account easily from Experience > Core Web Vitals:
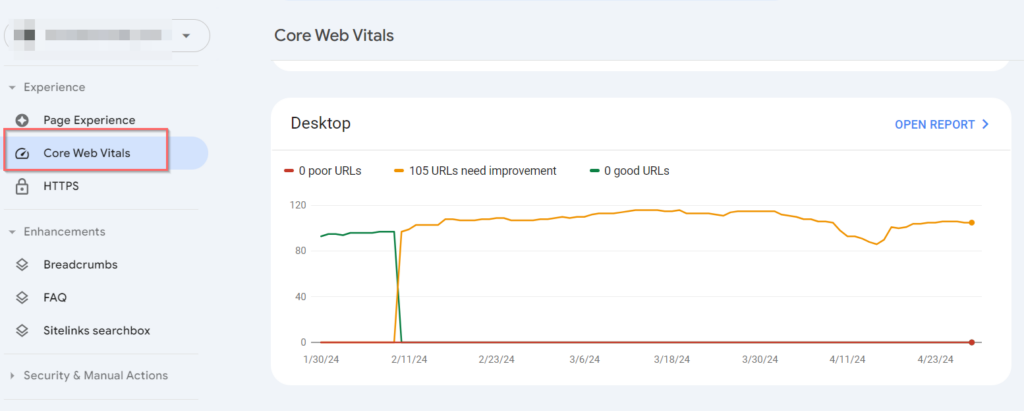
The report shows you pages in 3 categories for both mobile and desktop separately:
- Poor
- Need improvement
- Good
You’ll get to know which metric you need to improve to move your pages to a good category:
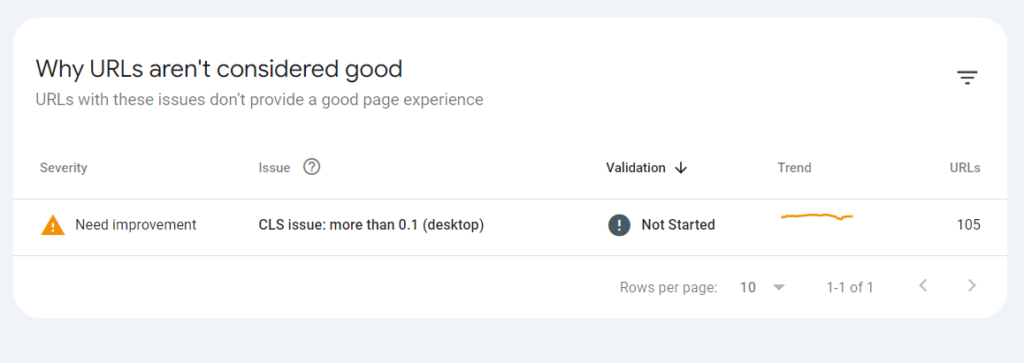
You can identify the pages that are impacted and take necessary action to improve them using the PageSpeed Insights tool that gives specific details on how to fix CWV issues.
It is an essential metric to track as it also impacts page load speed which plays a major role in UX, conversion, and search ranking. You can read more about CWV and how to track and improve it here.
4. Indexed Pages
It is an underrated SEO metric that most businesses and even marketers don’t look at too often. Indexed pages tell you how many pages (or URLs) a search engine has included in its index.
An index (of a search engine) refers to the database that contains the websites and pages that are found and available to serve. When a user enters a search query, the search engine looks for relevant content in its index and then serves relevant pages. Pages that aren’t added to the index won’t be served to the search users.
This is why it’s essential to have your website and its pages indexed. The indexed pages metric tells you how many URLs are indexed by a search engine. You can then expedite the indexing of pages that aren’t indexed yet.
Since it is a search engine related metric, you have to inspect indexed pages across different search engines. For Google, you can find indexed pages in Search Console under the Indexing tab:
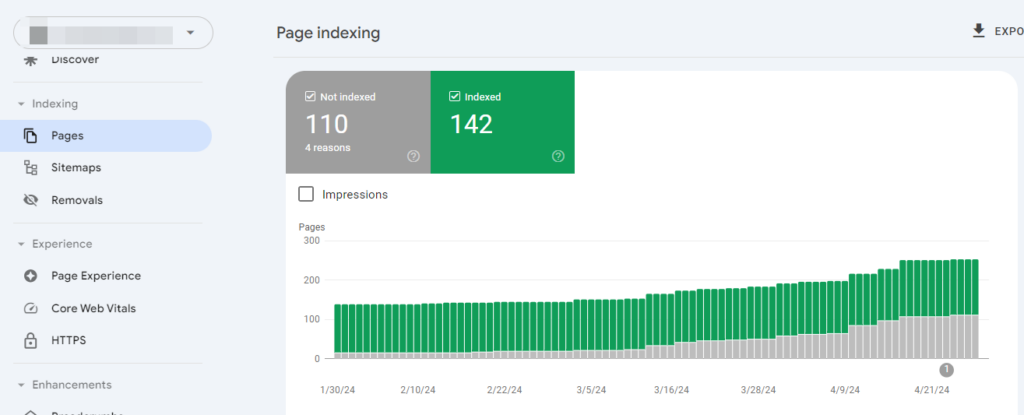
You can expedite indexing by submitting the URL inspection tab.
Similarly, Bing Webmaster Tools let you monitor indexed pages through Site Explorer:
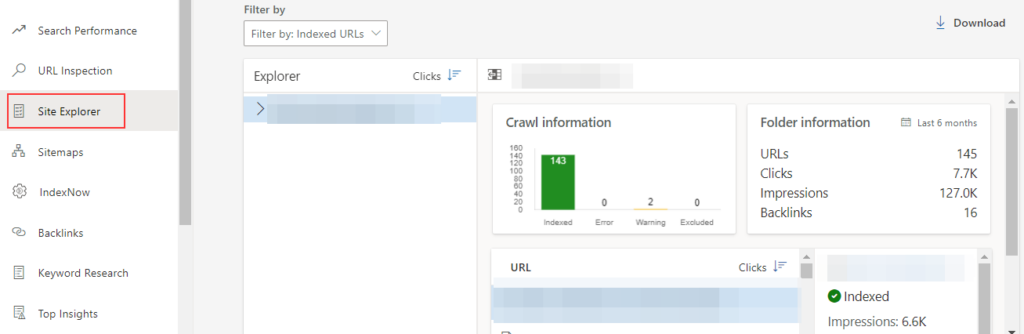
You can use the IndexNow tool to index new URLs automatically through your CMS (e.g., WordPress).
It is essential to constantly monitor indexed pages. It is an easy way to identify URL, navigation, and site structure related issues. In most cases, you have to submit new URLs for indexing to search engines. Keeping track of indexed pages helps you address issues on time.
5. Crawl Rate
It is another underrated SEO metric. Crawl rate goes hand in hand with indexed pages metric and both should be used together to make more sense of how search engines crawl and index your site and pages.
Crawling refers to the speed with which a website crawler visits your website to crawl and index content. Crawl rate refers to the number of visits a crawler makes to your website in a day. A high crawl rate means new and updated URLs and content is indexed quickly.
A high crawl rate doesn’t mean better search visibility, but it is an indication that your site is crawled multiple times a day without issues. It also indicates that new URLs are more likely to be crawled and indexed quickly.
You can check your crawl rate in Google Search Console in Settings:
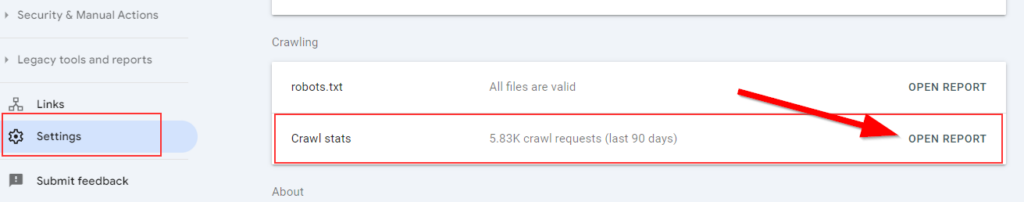
Open the report to check total crawl requests, download size, average response time, and several details including issues:
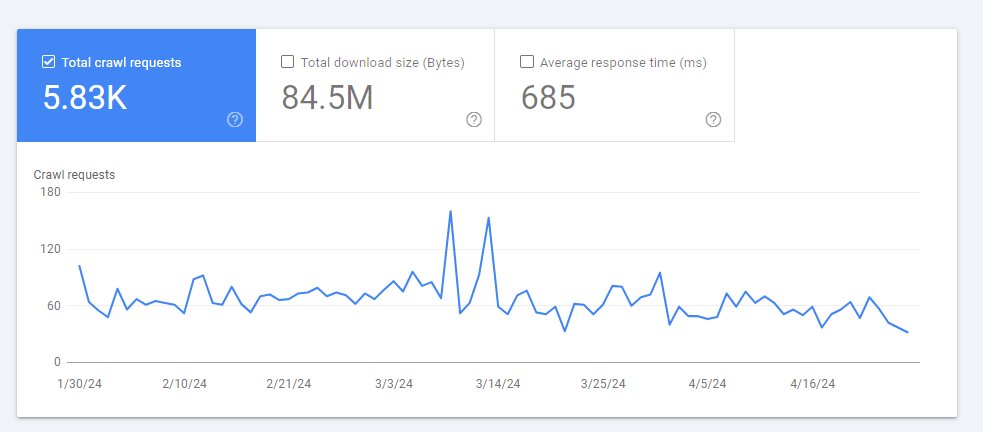
You can inspect daily crawl requests and how your website responds to these requests:
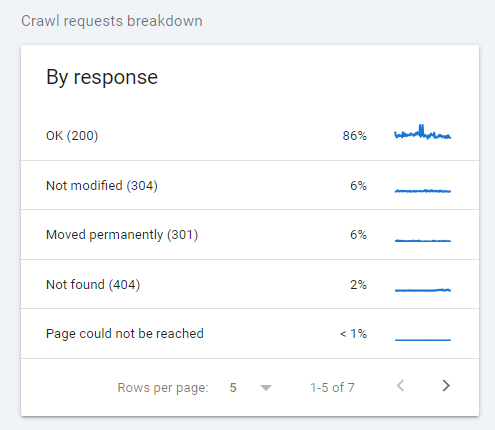
A crawl issue means bots can’t index new content and that’s the reason you should constantly monitor this SEO metric. You might publish new content daily, but if your crawl rate is too low, it’ll take ages to get it indexed.
You can use the URL inspection tool in Google Search Console to manually check the crawl status of individual URLs. If bots can’t crawl a URL, you’ll usually see an error code detailing how to fix it.
Bing Webmaster Tools goes a step further than Google and allows you to set your daily crawl rate through its Crawl Control tool. You get the option to choose a different crawl rate for every hour of the day. This gives you more flexibility and lets you optimize your crawl budget.
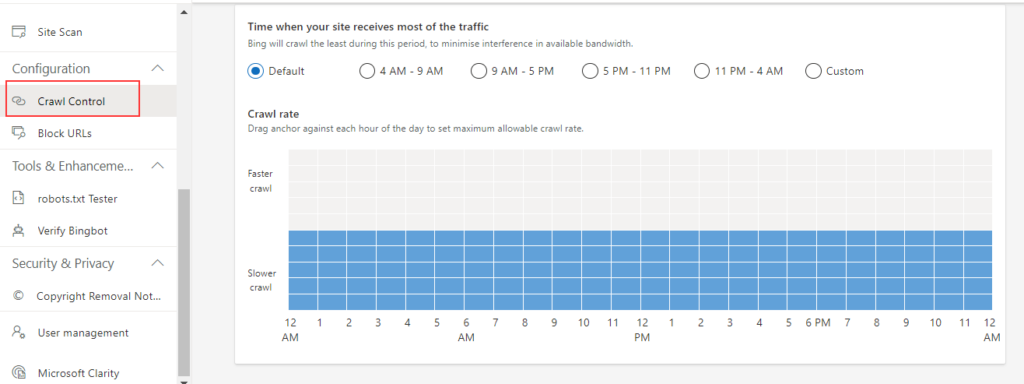
For example, if you publish new content in the morning or afternoon, you can increase the crawl rate for the morning and afternoon, and reduce it to a minimum for the rest of the day.
You can find crawl errors in Site Explorer using the filter at the top.
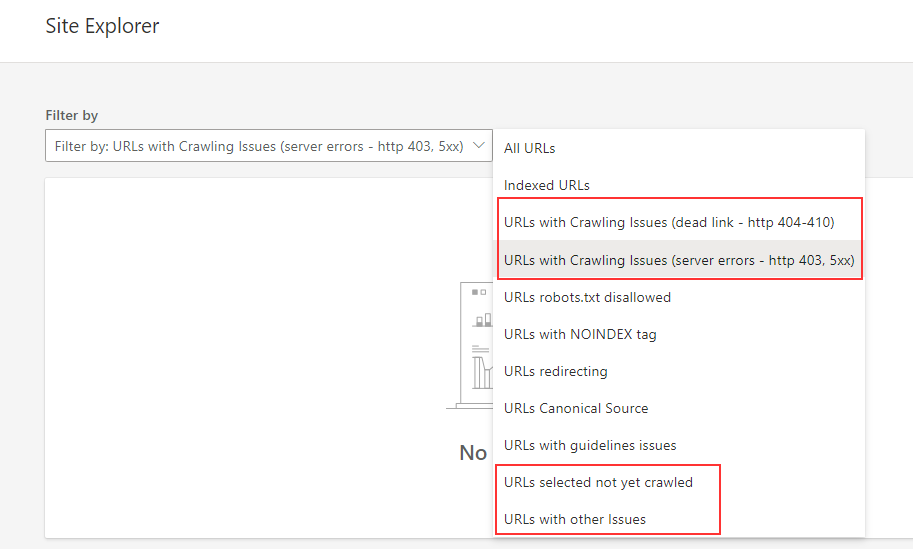
It helps you identify URLs with crawl errors and specific actions that you can take to fix the issue.
Keeping an eye on your crawl rate for major search engines will help you identify and fix search-related issues on time.
6. Engagement Rate
A primary SEO metric that’s available in Google Analytics 4 (GA4) is engagement rate. It tracks the overall engagement of users and reports it in the form of a percentage.
Engagement rate is defined as the percentage of engaged sessions on your website where an engaged session refers to any session that lasts longer than 10 seconds, has an event, or has at least 2 pageviews or screen views.
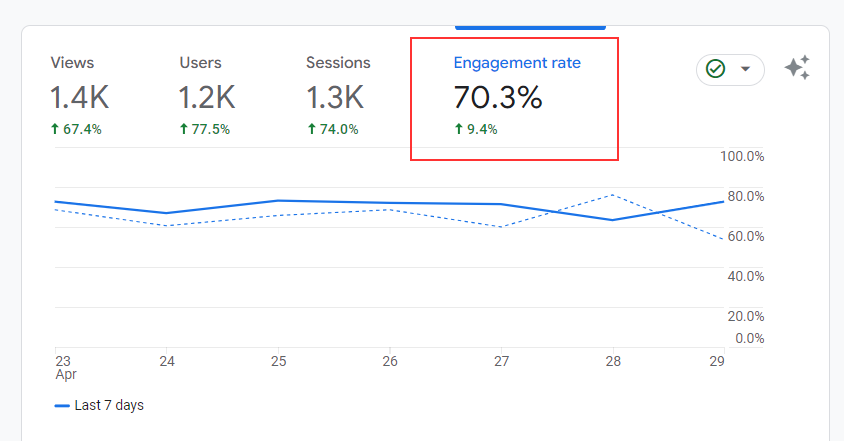
It tells you the percentage of visitors who interact with your website in a meaningful engagement. The remaining users are the ones who bounced back without any engagement (in less than 10 seconds).
If your website has a 70% engagement rate, 30% is your bounce rate.
Engagement and bounce rate work together and their total equals 100%.
Generally, if your engagement rate is higher than the bounce rate (more than 50%), it is a decent sign. The higher the engagement rate, the better.
It should be noted that the engagement rate indicates the overall percentage of engaged users, it doesn’t tell you the actual engagement events. This is a reason engagement rate must be used with other SEO metrics to identify issues (in case of a low engagement rate).
7. Backlinks
Backlinks are one of the most critical ranking factors. It is an essential SEO metric that plays a major role in your site’s ranking.
A study reported that top ranking pages in Google have more referring domains pointing to them than lower ranking pages. It is because Google considers backlinks as authenticity votes and a page having more votes means it’s popular and thus favored in SERPs:
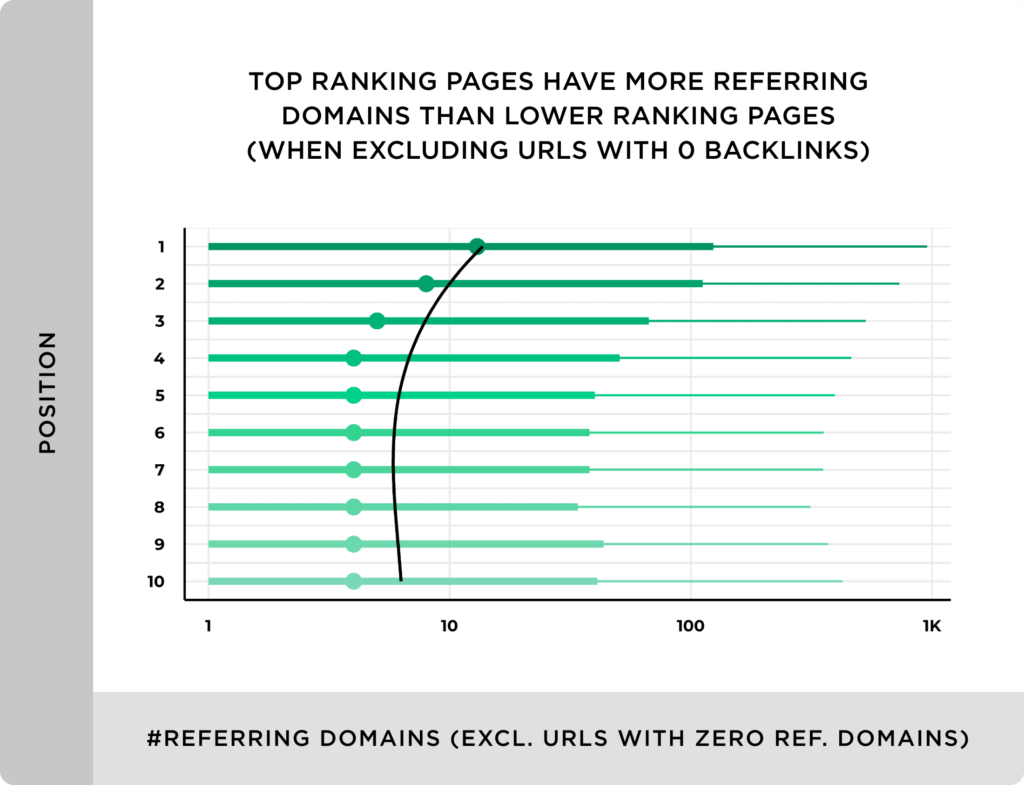
Simply having a high number of backlinks isn’t an indication of better search visibility. You need to track backlinks in 3 ways:
- The number of referring domains: You should have a high number of referring domains which means you should have backlinks from unique domains (not just one or a few domains).
- Authority of the domain: The authority of the domain is key. One backlink from a high authority website is better than having a hundred backlinks from low authority sites.
- Relevance of the linking domain: Backlinks from relevant domains are more valuable than links from unrelated domains.
Google Search Console also offers a free tool to monitor links. You can check referring pages, referring domains, linking pages, and target pages:
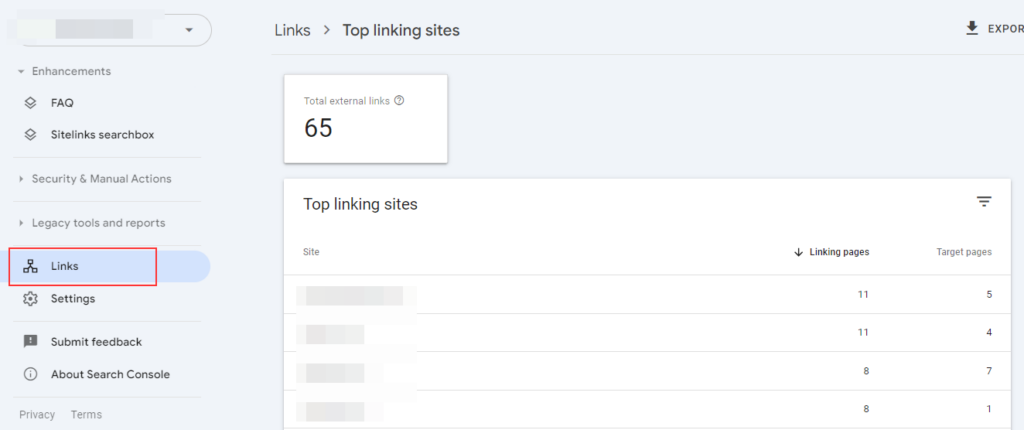
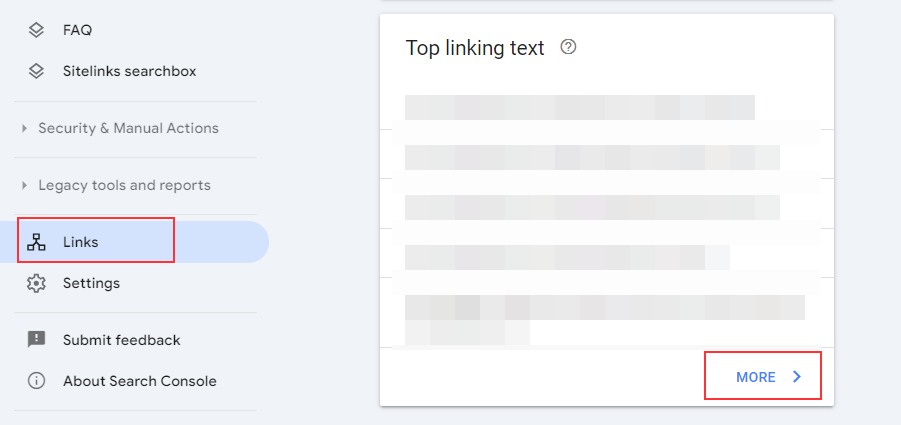
You can also check top linking text through Links in the search console:
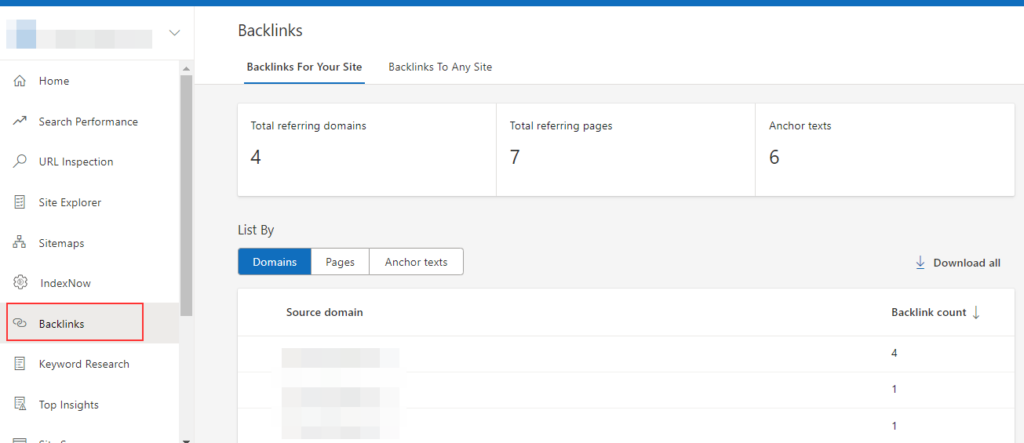
Bing Webmaster Tools also lets you monitor backlinks with domains, pages, and anchor texts:
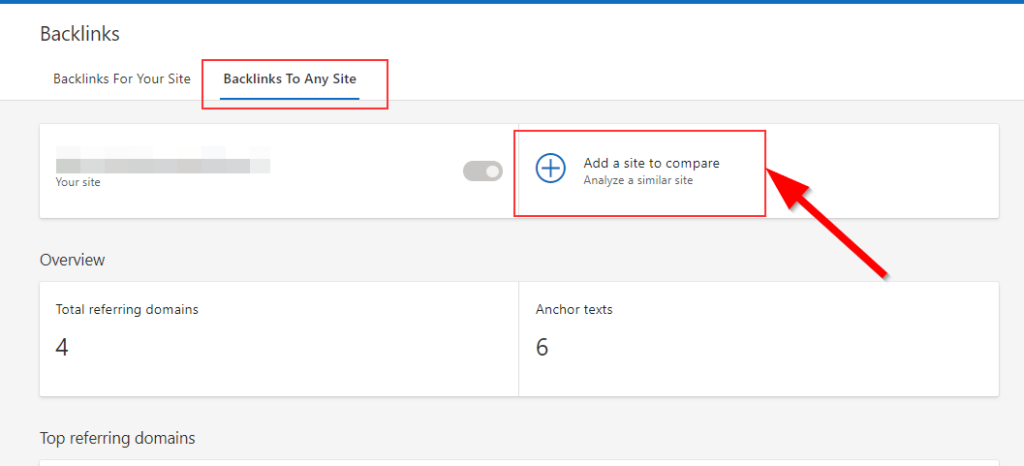
You can also check and compare backlinks of any website (e.g., your competitor) which is a free feature. This means you don’t have to own a website to check its backlink profile:
You can also use premium SEO tools like Ahrefs, Moz, Semrush, or others to monitor the backlink profile of your website. These tools scan your website regularly and report new backlinks that you acquire. You can evaluate links based on several factors such as link type, domain authority, page authority, relevance, domain age, and more.
Google identifies backlinks way too early than any of the paid tools because Google has an extremely massive index. Google Search Console should be your first option to monitor backlinks.
3 SEO Metrics You Shouldn’t Track
Not all SEO KPIs are worth measuring and relying on. Unfortunately, a lot of marketers end up wasting resources on tracking metrics that aren’t helpful. Here’s a list of the SEO metrics that you shouldn’t use for decision-making:
1. Traffic Value
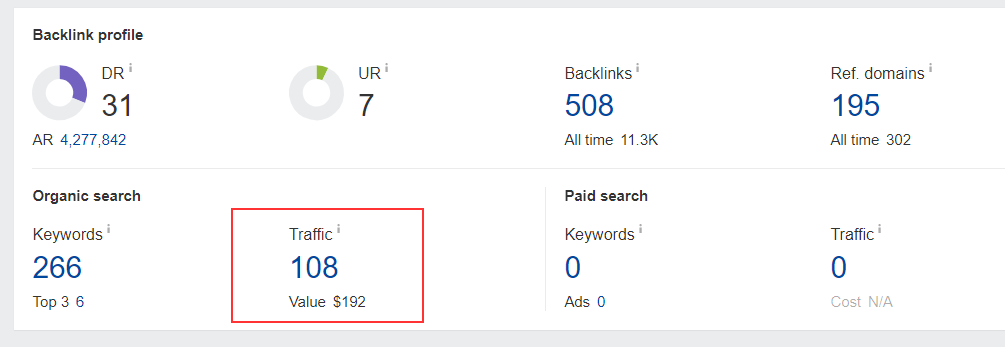
It is an overrated SEO metric that has not much to do with your site’s SEO performance. Traffic value refers to the total value of organic traffic your website receives.
It is a metric that’s used by keyword research and SEO tools like Ahrefs and Semrush. Ahrefs, for example, defines traffic value as: The equivalent monthly cost of traffic if that’s generated through a PPC campaign.
Here are a few reasons why you shouldn’t bother with traffic value and avoid making SEO decisions based on it:
- The value is determined by the average CPC of the keywords you are ranking for organically. You might rank for a lot of keywords that don’t have any value for your business
- It doesn’t tell you anything about SEO performance or ROI
- The traffic value itself isn’t 100% accurate and might be misleading (even if you decide to use it for decision-making).
For example, a traffic value of $500 doesn’t tell you anything about your site’s SEO performance. You might have a high traffic value, but your website might be doing exceptionally poor in SERPs. Or, you might have a low traffic value, but you might be ranking for some of the top keywords in your niche.
Though traffic value is calculated automatically by Ahrefs, Semrush, and other tools as it isn’t a paid tool, you should avoid using it to measure the SEO performance of your website.
2. Exit Rate
It is a useful SEO metric that’s reported by Google Analytics, but it is overrated and relative.
Google defines exit rate as the percentage of sessions that ended on a page or screen. Sessions ended on a page don’t necessarily mean a poor UX or poor SEO performance, it might be an indication that users get what they want from the page and leave it fully satisfied:

Exit rate alone is misleading and potentially useless as it doesn’t tell you the reason why those people are leaving your site from a particular page. It doesn’t tell you if they left satisfied or unsatisfied.
For example, a lot of people entering and exiting from a landing page with a signup form could mean they registered successfully and left the page.
You shouldn’t rely solely on exit rate as an SEO metric. Use it with other metrics to fully understand visitor journey and try to figure out if visitors are leaving satisfied or unsatisfied. One way to do it is through heat maps and session recordings that show how visitors interact with a web page.
3. Views per Session
It is a Google metric that’s reported in GA4 and it’s highly overrated, rather misleading.
Views per session is defined as the average number of web pages a user views within a session. It is reported in the form of an average number
Depending on the type and niche of your website, low views per session could mean a good thing. For example, if you have a blog with exceptionally long, detailed articles, views per session of around 1 is ideal because it indicates high engagement. It shows that visitors read the article without moving to another web page or clicking on any links.
Web pages that fulfill information intent should have low views per session while transactional intent pages should have high views per session.
If you look at the overall views per session metric, it tells you nothing unless you compare it with other metrics like engagement rate, bounce rate, time per screen, etc.
Avoid using the views per session metric for decision-making as it is relative.
Conclusion
In a world where search engines (especially Google) update their algorithm several times a year, it is essential to track the right SEO metrics to stay ahead of your game. There is no room for mistakes. You need to use your resources smartly by monitoring important KPIs.
The list of SEO metrics shared above is an absolute must.
And avoid the 3 KPIs that aren’t as useful.
It doesn’t cost you any money to track all the useless SEO metrics, but it does cost you a lot of time to interpret all of them. Smart marketers and businesses optimize their time.
Spend time on tracking what matters.
Featured Image: Pexels