There are two ways to drive traffic to your website. You can generate organic traffic or you can choose a paid traffic source. The paid traffic source is none other than Google Ads.
It is the most used ad network in the world that gives you access to multiple channels to generate traffic, leads, and sales for pretty much any business in any industry.
There are no limitations.
You can get started with as low as $5.
If you aren’t sure how and where to get started with Google Ads, this guide is for you.
What is Google Ads?
Google Ads, previously known as Google AdWords, is an advertising network by Google where businesses can run ad campaigns to reach their target audience. It’s primarily a pay per click (PPC) ad network that lets you run ads across Google products (such as search engine and YouTube) and to its wide network of sites and apps.
Here’s how Google Ads work for advertisers:
- You create an account with Google Ads for free
- Create your first campaign, ad group, and ad. You can do this during the onboarding process right after a new account registration
- Your ad goes live after review and you start receiving targeted traffic to your landing page.
Why Use Google Ads?
The top reasons why you should invest in Google Ads:
1. Biggest Global Ad Network
Google has the highest ad share of digital advertising revenue globally in 2023 and it’s the leading ad network:
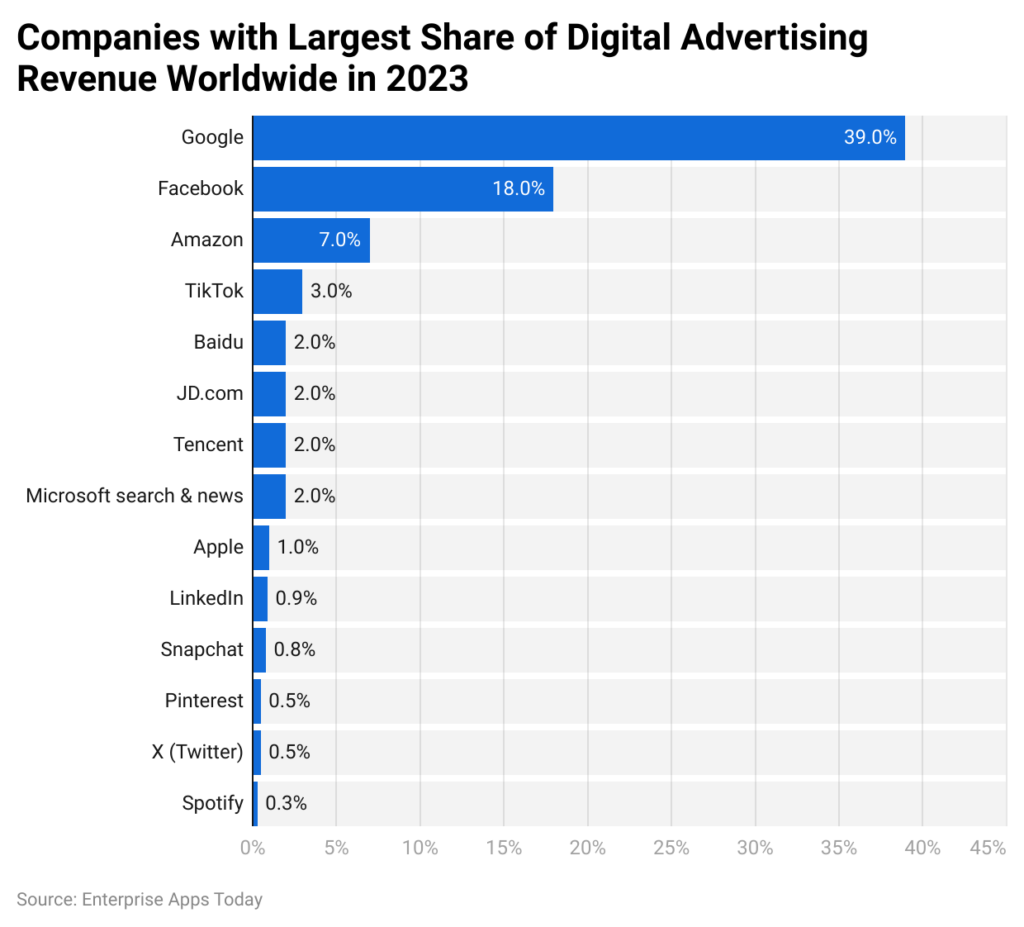
Since Google is the most used global search engine, it gives you access to a wider audience than most of the other ad networks (such as Meta).
You get global reach with Google Ads through its search engine, YouTube, and network of sites and apps. That’s something you don’t get with any other ad network.
2. Cost-Effective
Google Ads is quite cost-effective in both short and long terms.
The average CPC across all industries for search is $2.69 while for display ad network it’s $0.63:
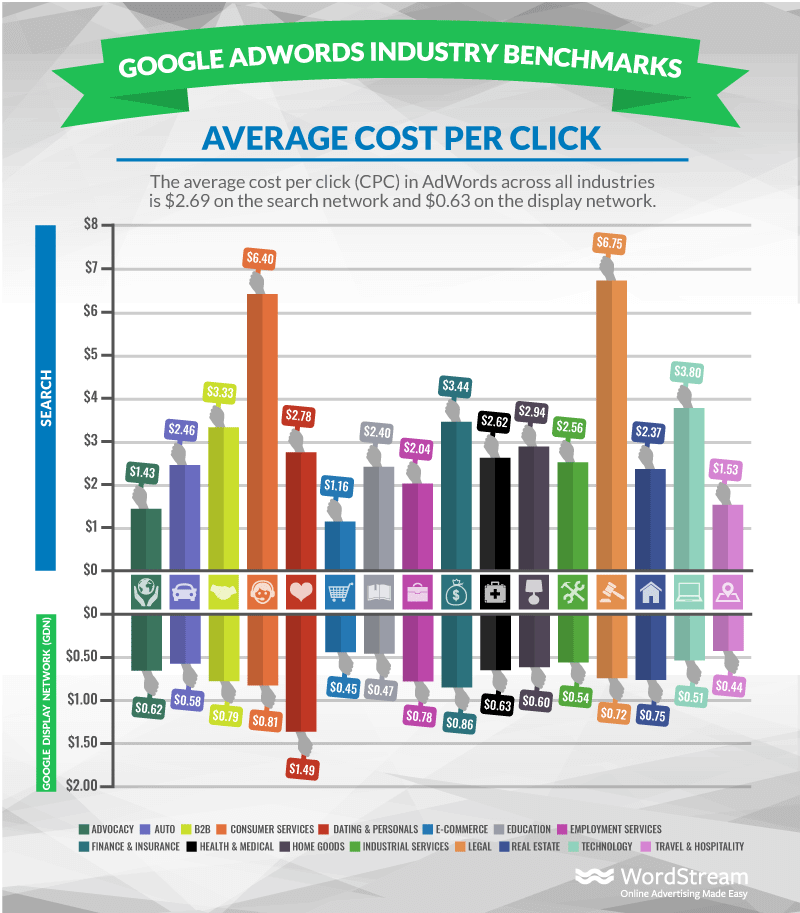
Depending on your industry, you might have to pay a high or low cost per click but the good thing is that everything is controllable. You can set a maximum cost per click or cost per conversion and pay whatever you want.
3. Instant Traffic
If you need instant traffic to a landing page, Google Ads work best. You’ll start receiving traffic as soon as your campaign goes live after review. Google reviews most ads in a single business day and in most cases, it takes a few hours.
This means you can start sending targeted traffic to any landing page on the same day.
Think of a pre launch campaign for a new product or a brand awareness campaign to reach a massive audience in a short period of time – Google Ads work best.
4. Multiple Ad Types
Google offers a wide range of ad types and formats. It gives you more options to choose from and reach your audience through different touchpoints using a single ad network.
The major ad types include:
- Search ads
- Display
- Video
- Shopping ads
- Local
- Local services ads
- App ads
- Smart ads
- Discovery
- Performance Max.
You can run ads across all Google products and services such as search engine, YouTube, Discovery, and others. Each ad type offers multiple types of ad formats to choose to make it easier for you to diversify creatives.
5. Easy to Get Started
One of the best things about Google Ads is that it doesn’t have any learning curve. You can get started immediately after signing up. The onboarding process helps you create your first campaign which is enough to help you get started.
You don’t have to necessarily hire an agency or someone to manage your Google Ads account, you can do it yourself hassle-free.
Additionally, Google offers lots of help articles including technical guides for advertisers. If you ever feel stuck or lost, you’ll find lots of helpful articles that make it easy to get back on track.
6. Advanced Targeting Options
Google Ads offers more than 15 different ways to target an audience. It includes advanced targeting options such as custom segments and your data segments:
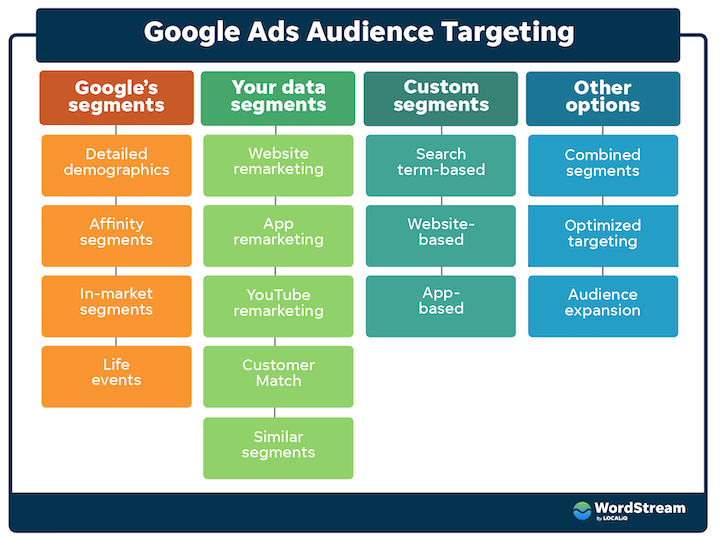
What sets Google Ads targeting apart from other ad networks is its ability to target people based on their in-market behavior. For instance, you can reach people who are actively looking to buy a specific product. This data is available to Google based on a user’s search history.
This is one area where social ads lack as they don’t have such precise data about users’ buying patterns.
7. Full Control
You get full control over budgeting, ads, campaigns, and everything through your Google Ads account. You can cap your daily budget, you can increase or decrease bids based on keyword or ad performance, and you can pause campaigns whenever you want to.
Control over ad spending is the key here. You control how much you can afford to pay per click, mile, or action. Google Ads sticks to your spending limit strictly.
Google Ads Types
It provides a wide range of ad types to advertisers and businesses. Let’s explore the types of ads and when to use them:

Search Ads
These ads appear in Google search results. These ads are suitable for all types of businesses as they help you reach your target audience through Google search. You can target people based on keywords, devices, location, and other targeting options.
Display Ads
These ads are shown on websites and apps that are part of Google Display Network which has more than 3 million sites and apps. These ads are ideal for brand awareness and reaching people based on what websites they visit.
Shopping Ads
These are special types of search ads that promote your products to searchers. These ads are suitable for ecommerce businesses that sell physical goods either locally or internationally.
Video Ads
These are short or long video ads that mostly appear on YouTube (and can be shown at other places too like the Display network). Video ads work best for all types of businesses as they are visually pleasing and more engaging than text or image ads.
App Ads
These are specifically made for businesses that sell apps. Ads are aimed at generating app downloads or boosting app engagement.
These ads appear at different locations including Search, YouTube, Google Play, and other channels. If you have an app you want to promote, Google App Ads is your best bet.
Discovery Ads
These ads appear on feeds such as Gmail, YouTube, and Discover. The ads help you drive more sales and boost the discovery of your offers.
Local Services Ads
These are lead generation ads that help local service providers receive more calls. These ads require a Google Business Profile and verification process before your ads can appear in search.
Smart Ads
These are automated ads that are run and managed by Google. Your ads appear at different locations based on your settings. Smart ads are ideal for businesses that want to reach their audience through different channels and figure out what type of ads work best so they can narrow down.
Performance Max
These are automated AI-powered ads. It is an advanced version of Smart Ads that uses different assets and automatically creates new assets based on existing ones.
These ads run across Google network and products with a focus on reaching your goal (such as conversions or clicks). The AI can create any type of ad and place it anywhere if it thinks it will help you achieve your goal. These automated ads work best for businesses that want their campaigns to run automatically without any supervision.
How to Get Started with Google Ads?
Now that you know the basics of Google Ads, let’s see how you can get started for the first time and have your account ready.
1. Sign up
Click here to visit the official Google Ads site and click Start now:

You can sign up with your existing Google Account and create an ad account with a single click. You’ll then be taken to the onboarding process. As part of the onboarding process, you have to create your first campaign (Smart campaign).
Follow the on-screen instructions and create your first campaign. This will help you better understand how Google Ads work. You can pause or delete this campaign later. The idea is to get used to Google Ads.
It’s, however, recommended to skip the onboarding process by clicking Switch to Expert Mode to create your campaign from scratch:
You can follow the steps below to create a campaign from scratch based on your requirements.
Step #2: Create a New Campaign
Click the Create button and select Campaign:
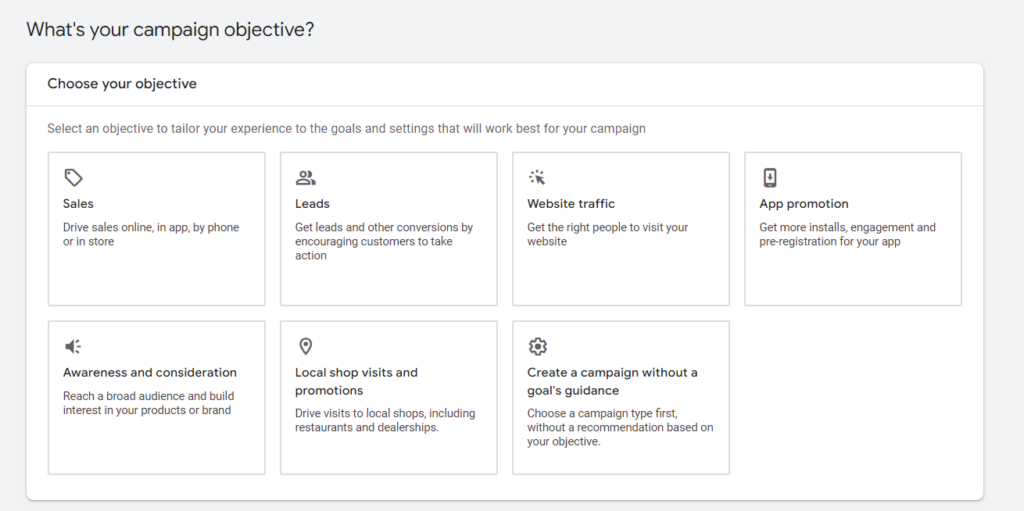
Choose your objective based on your advertising goal and what you want to achieve. The common objectives include sales, leads, and website traffic:
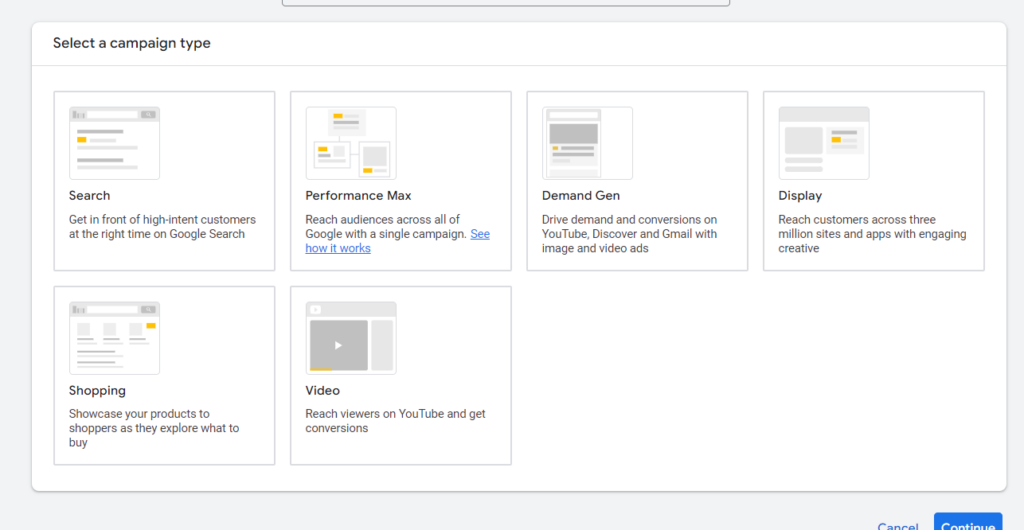
Once you choose an objective, you will see relevant campaign types (or ad types as discussed above). Select the most appropriate type:
Add URL, campaign name, and other relevant details and click Continue. The details you have to add here depend on the campaign objective and type.
Step #3: Campaign Settings
Next, you have to customize your campaign’s settings by adding bidding details, keywords and assets, creating ads and ad groups, setting a budget, and tweaking campaign settings.
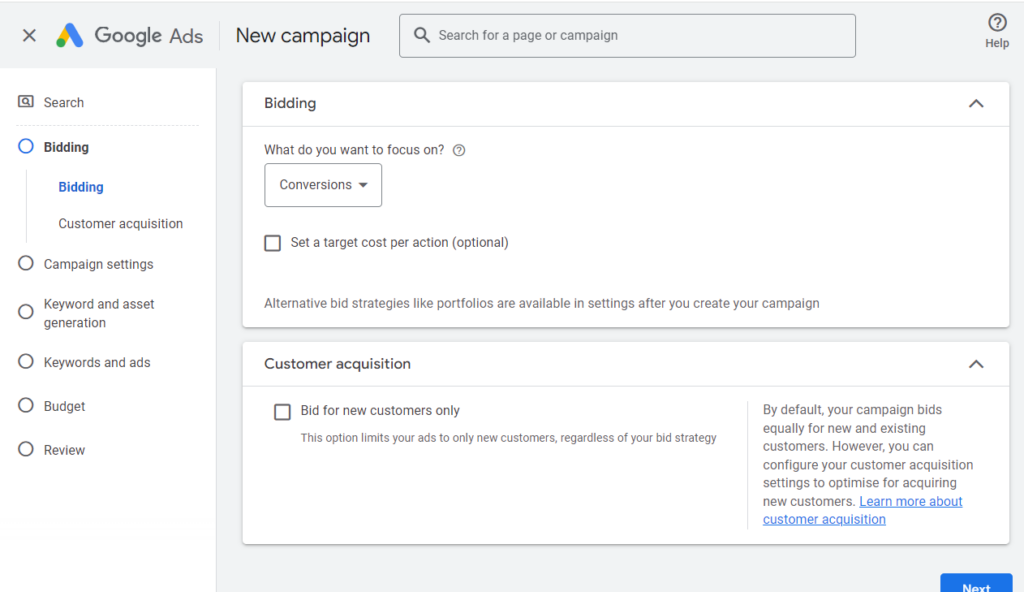
Campaign assets, bidding strategy, ads, ad groups, and other settings vary for different campaign types. For instance, for search campaigns, you have to add keywords and create text-based ads for Google Search. If you have a display campaign, you’ll be asked to upload banner ads based on specific requirements.
The good thing is that Google Ads uses AI to help you create ads and manage assets. You’ll see optimization scores of your ads that help you improve quality and targeting.
When setting a campaign budget, you’ll be asked to add a payment method. Add your payment details and choose a charge method. You can add funds to your account if you don’t want to get your card auto-charged.
Step #4: Submit and Wait for Approval
After setting everything, review your campaign, ad groups, and ads. Publish your campaign.
It won’t go live immediately, rather it’ll first be reviewed. If there are any objections or revisions required, you’ll be asked to tweak relevant parts of your campaign.
Once your campaign is approved, it’ll go live.
Some campaign types such as Smart and Performance Max need time to show results as they need time to understand your audience. In other cases, you’ll see traffic reports in 1-2 days.
Keep an eye on the recommendation section. It tells you what actions you can take to improve campaign performance to achieve your goals.
Google Ads Best Practices
Creating Google Ads campaigns is the beginning. There’s a lot to do to optimize your campaigns and budget. Here’s a list of proven Google Ads best practices that you should follow to improve ad performance:
1. Choose the Correct Campaign Objective and Type
Google Ads does a good job of describing campaign objectives and types to help you choose the correct option.
But, it’s not that straightforward – all the time.
You should have a well-defined goal for your ad campaign such as driving traffic to a landing page or generating 500 sales in 30 days.
Then identify your goal with a campaign objective and choose the most relevant campaign type.
You can only do this if you have well-defined advertising goals for your business. It’ll help you track performance and see how successful your campaign is.
2. Organize Your Ad Account
You should keep your ads account organized from day one. Maintain an account structure with well-defined campaigns, ad groups, and ads.
Here’s an example of how to organize your Google Ads account:
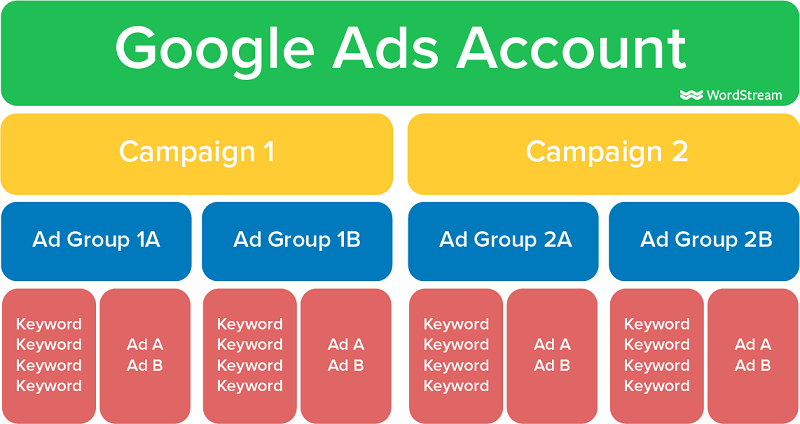
A single campaign should have no more than 15 ad groups and each ad group should have a maximum of 5 ads. This will help you keep things manageable.
Minimizing the number of ad groups in each campaign and the number of ads in each ad group helps you better understand ad performance. It also gets easier to optimize ads and ad groups.
When you start with a new Google Ads account, you have limited campaigns. You don’t feel the need to have a well-structured account. But as your ad account grows (and sure it does), you’ll have numerous campaigns running simultaneously each with several ad groups and ads.
That’s where you will feel the need to have an organized account structure.
It’s recommended to keep it manageable from day one.
3. Align the Ad, Landing Page, and Offer
Aligning ad copy with a landing page is an essential part of optimization.
You need to set clear and accurate expectations via your ad. When visitors click your ad and visit the landing page, they should get exactly what they expect. The offer on the landing page needs to be the same as advertised.
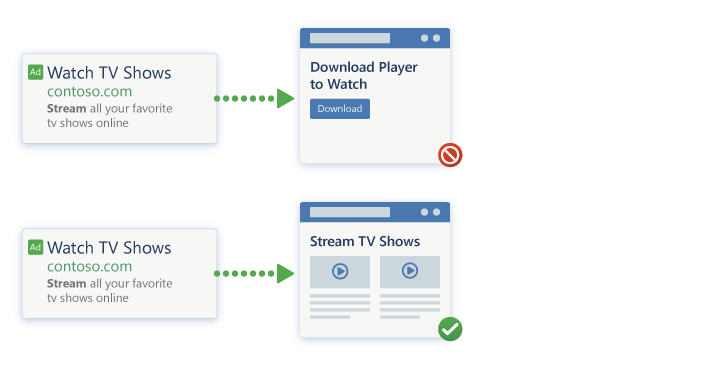
If your ad copy isn’t relevant to the landing page or offer, you’ll have a low conversion rate. This is because your audience won’t get what they expect on the landing page and will leave immediately.
You need to provide as many details as possible in the ad. This includes offer, price, shipping details, review, benefits, etc. The content on the landing page and ad should be aligned on a regular basis.
Misaligned ad and landing page would also lead to ad rejection by Google Ads. Avoid doing it, especially in cases where you are trying to promote a product that’s restricted or prohibited by Google Ads (see this list). Advertisers try to game the system by sending traffic to a prohibited product by not disclosing the offer in the ad copy or adding false information.
You need to avoid such practices for two reasons:
- In most cases, your ad won’t be approved and you might get your ads account banned for repeated violations
- Even if your ad gets approved, you’ll end up having a significantly low conversion rate with high traffic. This leads to a poor UX that leads to high CPC and poor quality score.
Stick with the basic rule: Ad copy must align with the landing page and both should talk about the same, single offer.
4. Use Dedicated Landing Pages
A landing page is a special type of marketing page used for lead generation. You need to send traffic from ads to dedicated landing pages that are specifically created for collecting visitors’ information so they enter your sales funnel.
Sending paid traffic to a sales page, product page, home page, or any other page on your site creates distraction and leads to a low conversion rate.
A typical landing page has a conversion rate between 6-10% while some landing pages are reported to have up to 25% conversion rate. The average conversion rate of a website is around 2.35% while top websites convert in the range of 10%.
That’s a lot of difference.
The main reason is that landing pages are highly personalized, promote one offer, have minimal friction and distractions, and don’t (necessarily) sell anything.
Here’s an example of a landing page:
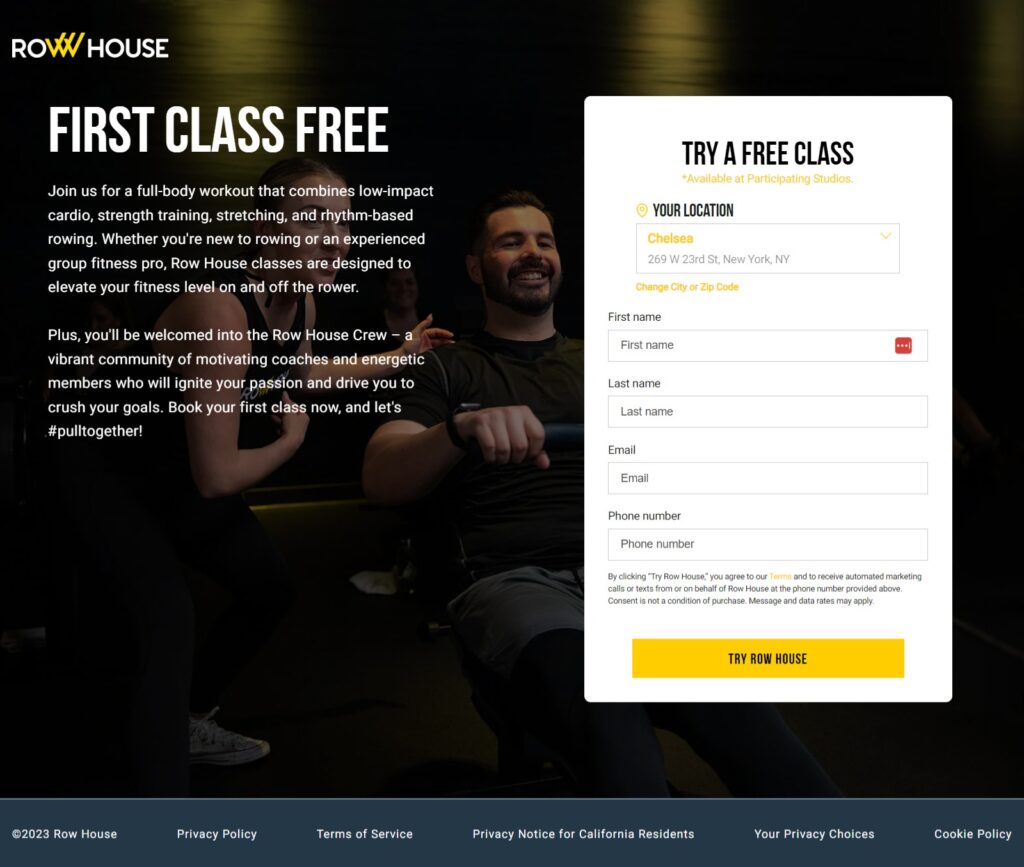
A potential customer is more likely to share personal details in exchange for a highly valuable free lead magnet than buying a product from a brand right away.
It’s an absolute must to send traffic from ads to a dedicated landing page that:
- Has a single offer
- Has a clear CTA
- Doesn’t sell or presell anything (unless you are targeting the BOFU audience)
- Offers a high value lead magnet
- Aligns perfectly with the ad copy.
5. Start with Broad Match
Keywords play a critical role in Google Ads, especially for search ads. You need to target the right keywords to reach the right people.
Google Ads has 3 types of keyword match types to choose from:
- Broad match
- Phrase match
- Exact match.
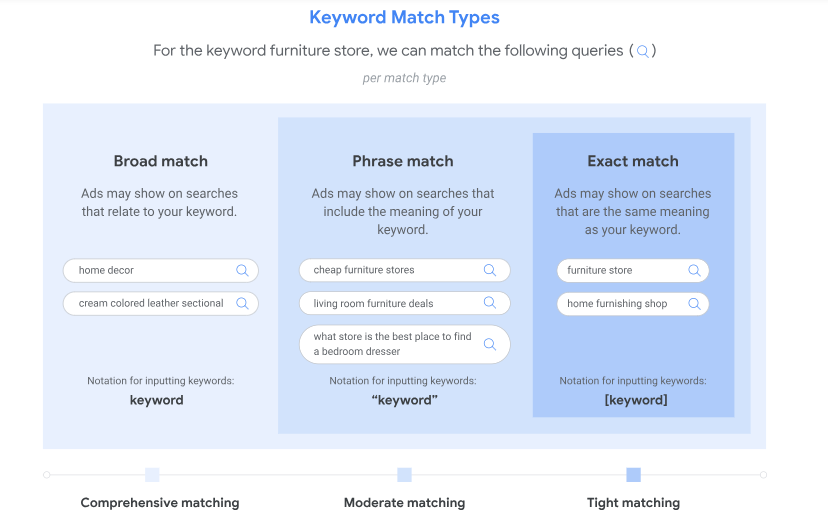
Broad match is the default setting for all keywords which means your ads will trigger all the related search queries even if the exact keyword isn’t present in the search query.
Here’s an example of a broad keyword match by Google:
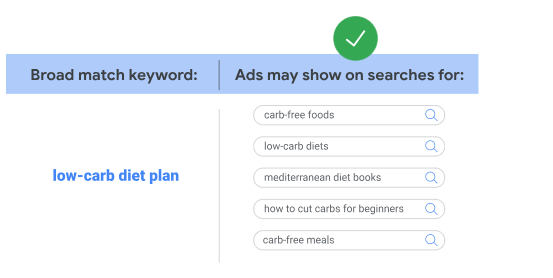
Phrase match triggers your ads for keywords that include the meaning of your keywords and exact match shows your ads for the exact keywords that have the same meaning.
Ideally, you should start with a broad match to reach a wider audience. You can identify relevant keywords that drive conversions and channelize your spending.
Once you have identified a list of high converting keywords through broad match type, you can then switch to phrase match to narrow down further.
And finally, you can stick to creating exact match type campaigns for the best keywords that convert exceptionally well.
6. Create a Negative Keyword List
For any ad campaign that has keywords, you need to add a negative keyword list. These negative keywords exclude certain words and phrases that don’t trigger your ads. Your ads won’t trigger for keywords added in the negative keyword list:
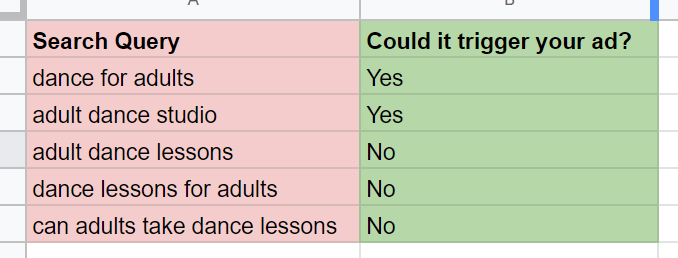
When you run a search campaign with a broad match type, your ads might trigger for irrelevant search terms. Such search terms need to be analyzed and added to negative keywords so your ads don’t trigger for similar keywords in the future.
Similarly, you’ll notice that some keywords lead to low conversion rate for numerous reasons. You need to stop showing your ads for keywords that don’t drive targeted traffic or send low-converting traffic due to search intent mismatch or any other reason.
For instance, your ads might trigger for ‘free team collaboration tool’ if you are using a broad match type for the keyword ‘team collaboration app’. If your app isn’t free, you’ll see a lot of clicks with no conversions as people click your ad to get a free team collab tool and if your tool isn’t free, they’ll leave immediately.
In this case, you need to add ‘free’ to the negative keyword list by selecting an appropriate match type (ideally broad match) so that your ads don’t trigger for any keyword that contains the word ‘free’.
You can create an account level negative list that applies to all the campaigns once you have a decent list of negative keywords. This is quite helpful as new campaigns won’t trigger for irrelevant keywords leading to optimized spending.
Click Tools > Shared library > Exclusion lists > Negative keyword lists to add negative keywords:
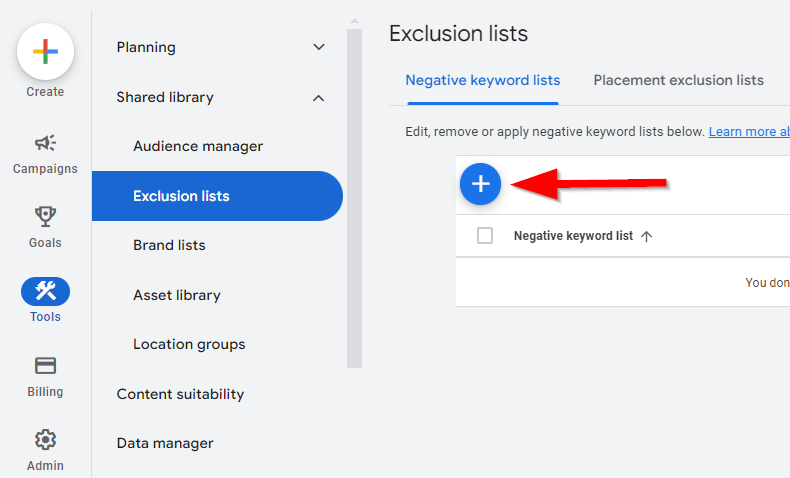
You can create multiple lists and tweak them easily.
7. A/B Test Everything
Google Ads require a lot of testing and tweaking. Creating an ad campaign is one thing and getting conversions and improving ROAS is a different thing.
Even if your campaign starts sending traffic, you’ll still need to optimize it to improve its performance.
This requires A/B testing everything ranging from ad copy, headlines, images, landing page elements, offer, targeting, campaign types, and much more.
Experimentation has multiple benefits:
- Ad and campaign performance improvement
- Better ROI and ROAS
- Replication gets easier because you know what’s working
- Better understanding of your ideal customers
- Insights and data that can be used across marketing campaigns.
Check out this detailed guide on A/B testing for more details.
Final Words
Google Ads offers everything you need to grow your business. The hard part, however, is that it isn’t a set-and-forget traffic generation method.
You need to actively supervise and manage Google Ads campaigns.
It also has a learning curve if you want to up your advertising game.
This guide has everything you need to kickstart your Google Ads journey. With A/B testing, you can get targeted traffic, generate conversions, and improve ad performance. Once you start seeing a positive ROI and ROAS, you’ll fall in love with PPC.
Featured Image: Pexels